Overview
When you use button, you can not only press down the button, light on the LED, release the button, turn off the LED, but also can switch the working state of the LED every time the button is pressed. In order to achieve this effect, you need to know when the state of the button changes from off to on, that is, “state change detection”. In this lesson, we will print the results of state change detection of the button in the serial monitor.
Components Required
Note: Refer to Part 2 to check details of hardware.
Fritzing Circuit
In this example, we use pin 2 to read the signal of the button.
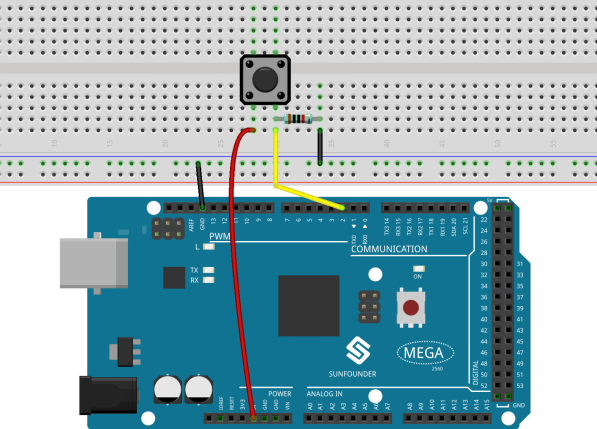
Schematic Diagram

Code
const int buttonPin = 2;
int detectionState = 0;
int buttonState = 0;
int lastButtonState = 0;
void setup()
{
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
if (buttonState != lastButtonState)
{
if (buttonState == HIGH)
{
detectionState=(detectionState+1)%2;
Serial.print("The detection state is:");
Serial.println(detectionState);
}
delay(50);
}
lastButtonState = buttonState;
}After the codes are uploaded into the Mega2560 board, the output number will switch between 0 and 1 every time you press the button.
Code Analysis
Declare a pin connected to Button.
const int buttonPin = 2;Declare a variable called 「detectionState」to record every state of state change detection.
const int buttonPin = 2;Declare two variables to read the state of the button for state change detection.
int buttonState = 0;
int lastButtonState = 0; In setup(), initialize the pins and then start up the serial monitor.
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);In loop(), read the value of buttonPin and then assign to the variable buttonState.
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);Compare buttonState with lastButtonState, if they are not equal, it indicates that the state is changed. A delay(50) is needed to realize debouncing during the changing detection. After comparison, assign the buttonState to lastButtonState to make the next round of judgment.
if (buttonState != lastButtonState)
{
...
delay(50);
}
lastButtonState = buttonState;The state change judgment installed (buttonState != lastButtonState), the further judgment is made to get the condition「Press the button」.
if (buttonState == HIGH)
{
...
} Under the state「Press the button」, detectionState is being operated and it switches between 1 and 0.
Meanwhile, the value of detectionState is printed.
detectionState=(detectionState+1)%2;
Serial.print("The detection state is:");
Serial.println(detectionState);Phenomenon Picture
