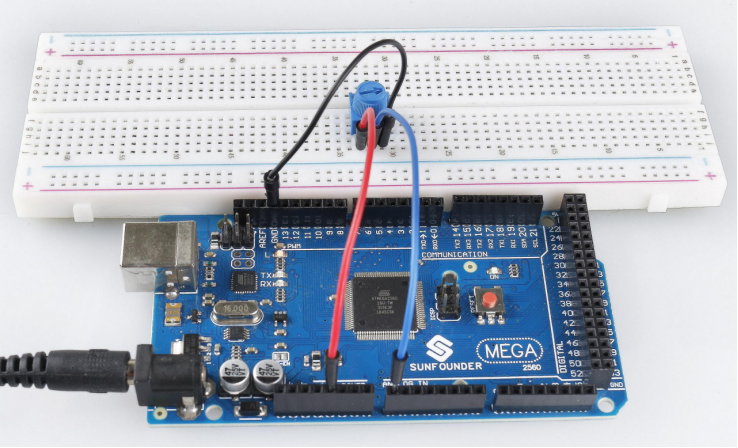
Overview
You can use the analogRead() command to read analog input from the physical world through an analog pin, which is suitable for analog input elements such as potentiometers, photoresistance, water level detection sensors, and so on. This article will take the potentiometer as an example to read the analog value of its output.
Components Required
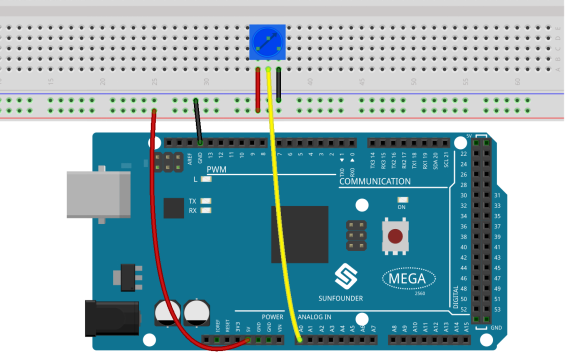
Fritzing Circuit
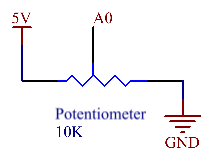
In this example, we use the analog pin (A0) to read the value of the potentiometer. Connect the pins at both ends of the potentiometer to 5V and GND respectively. Connect the middle pin to A0.
The voltage of the middle pin will be output to the Mega2560 board as an analog value. By rotating the axis of the potentiometer, you can change the voltage on the middle pin, thereby changing the analog value of the pin obtained by A0.
Schematic Diagram
Code
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop()
{
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
Serial.println(sensorValue);
delay(1);
}After the code is uploaded to the Mega2560 board, you can open the serial port monitor to view the reading value of the pin. When the shaft of the potentiometer is turned, the serial port monitor will print the value that changes between “0” and “1023”.
Code Analysis
To enable Arduino IDE to print the value transmitted from electronic component to the Mega2560 board, you need to start serial communication in setup() and set the data rate to 9600.
Serial.begin(9600);Use the analoglRead() statement in loop() to read the level state acquired by analog pin A0 and declare a variable to store the level state.
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);Print the value stored in the variable on the serial monitor.
Serial.println(sensorValue);Use delay() statements to make printing results easy to observe.
delay(1); ※ Analog-to-Digital Converter
The Arduino have a circuit inside called an analog-to-digital converter or ADC that reads this changing voltage and converts it to a number between 0 and 1023. When the shaft is turned all the way in one direction, there are 0 volts going to the pin, and the input value is 0. When the shaft is turned all the way in the opposite direction, there are 5 volts going to the pin and the input value is 1023. In between, analogRead() returns a number between 0 and 1023 that is proportional to the amount of voltage being applied to the pin.
Phenomenon Picture