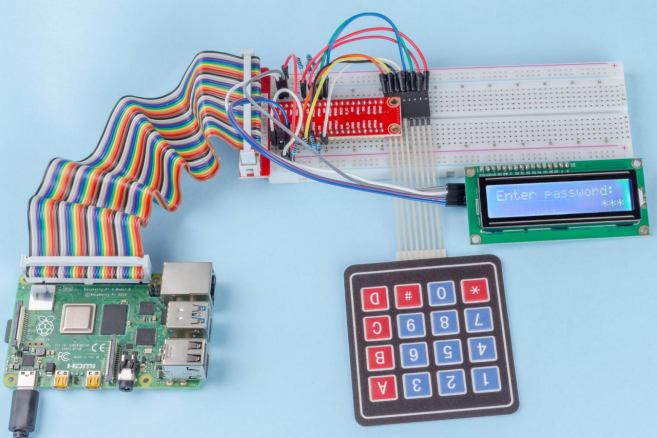
Introduction
In this project, we will use a keypad and a LCD to make a combination lock. The LCD will display a corresponding prompt for you to type your password on the Keypad. If the password is input correctly, “Correct” will be displayed.
On the basis of this project, we can add additional electronic components, such as buzzer, LED and so on, to add different experimental phenomena for password input.
Components
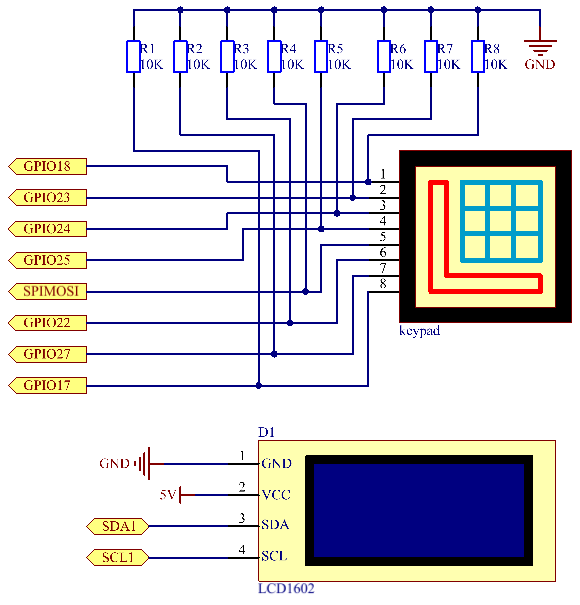
Schematic Diagram
| T-Board Name | physical | wiringPi | BCM |
| GPIO18 | Pin 12 | 1 | 18 |
| GPIO23 | Pin 16 | 4 | 23 |
| GPIO24 | Pin 18 | 5 | 24 |
| GPIO25 | Pin 22 | 6 | 25 |
| GPIO17 | Pin 11 | 0 | 17 |
| GPIO27 | Pin 13 | 2 | 27 |
| GPIO22 | Pin 15 | 3 | 22 |
| SPIMOSI | Pin 19 | 12 | 10 |
| SDA1 | Pin 3 | ||
| SCL1 | Pin 5 |
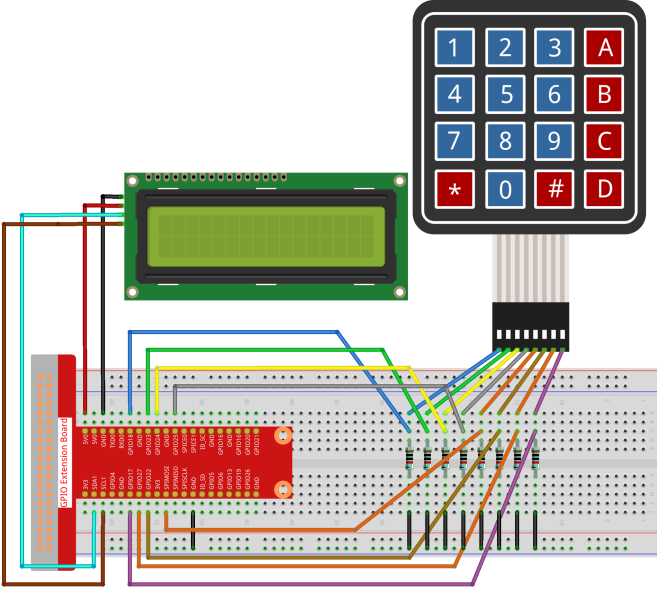
Experimental Procedures
Step 1: Build the circuit.
- For C Language Users
Step 2: Change directory.
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/c/3.1.9/Step 3: Compile.
gcc 3.1.9_PasswordLock.cpp -lwiringPiStep 4: Run.
sudo ./a.outAfter the code runs, keypad is used to input password. If the “CORRECT” appears on LCD1602, there is no wrong with the password; otherwise, “WRONG KEY” will appear.
Code Explanation
#define ROWS 4
#define COLS 4
#define BUTTON_NUM (ROWS * COLS)
#define LENS 4
unsigned char KEYS[BUTTON_NUM] {
'1','2','3','A',
'4','5','6','B',
'7','8','9','C',
'*','0','#','D'};
char password[LENS]={'1','9','8','4'};Here, we define the length of the password LENS, storage matrix keyboard key value array KEYS and the array that stores the correct password.
void keyRead(unsigned char* result);
bool keyCompare(unsigned char* a, unsigned char* b);
void keyCopy(unsigned char* a, unsigned char* b);
void keyPrint(unsigned char* a);
void keyClear(unsigned char* a);
int keyIndexOf(const char value);There is a declaration of the subfunctions of the matrix keyboard code, refer to chapter 2.1.5 of this document for more details.
void write_word(int data);
void send_command(int comm);
void send_data(int data);
void lcdInit();
void clear();
void write(int x, int y, char const data[]);There is a declaration of the subfunctions of LCD1062 code, refer to chapter 1.1.7 of this document for more details.
while(1){
keyRead(pressed_keys);
bool comp = keyCompare(pressed_keys, last_key_pressed);
……
testword[keyIndex]=pressed_keys[0];
keyIndex++;
if(keyIndex==LENS){
if(check()==0){
clear();
write(3, 0, "WRONG KEY!");
write(0, 1, "please try again");
}
……Read the key value and store it in the test array testword. If the number of stored key values is more than 4, the correctness of the password is automatically verified, and the verification results are displayed on the LCD interface.
int check(){
for(int i=0;i<LENS;i++){
if(password[i]!=testword[i])
{return 0;}
}
return 1;
}Verify the correctness of the password. Return 1 if the password is entered correctly, and 0 if not.
- For Python Language Users
Step 2: Change directory.
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python/Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 3.1.9_PasswordLock.pyAfter the code runs, keypad is used to input password:1984. If the “CORRECT” appears on LCD1602, there is no wrong with the password; otherwise, “WRONG KEY” will appear.
Code Explanation
LENS = 4
password=['1','9','8','4']
……
rowsPins = [18,23,24,25]
colsPins = [10,22,27,17]
keys = ["1","2","3","A",
"4","5","6","B",
"7","8","9","C",
"*","0","#","D"]Here, we define the length of the password LENS, the array keys that store the matrix keyboard keys, and the array password that stores the correct password.
class Keypad():
def __init__(self, rowsPins, colsPins, keys):
self.rowsPins = rowsPins
self.colsPins = colsPins
self.keys = keys
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(self.rowsPins, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.setup(self.colsPins, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN)
...This class is the code that reads the values of the pressed keys. Refer to chapter 2.1.5 of this document for more details.
while(True):
pressed_keys = keypad.read()
if len(pressed_keys) != 0 and last_key_pressed != pressed_keys:
LCD1602.clear()
LCD1602.write(0, 0, "Enter password:")
LCD1602.write(15-keyIndex,1, pressed_keys)
testword[keyIndex]=pressed_keys
keyIndex+=1
...Read the key value and store it in the test array testword. If the number of stored key values is more than 4, the correctness of the password is automatically verified, and the verification results are displayed on the LCD interface.
def check():
for i in range(0,LENS):
if(password[i]!=testword[i]):
return 0
return 1Verify the correctness of the password. Return 1 if the password is entered correctly, and 0 if not.
Phenomenon Picture