Introduction
Servo is a type of geared motor that can only rotate 180 degrees. It is controlled by sending electrical pulses from your SunFounder board. These pulses tell the servo what position it should move to.
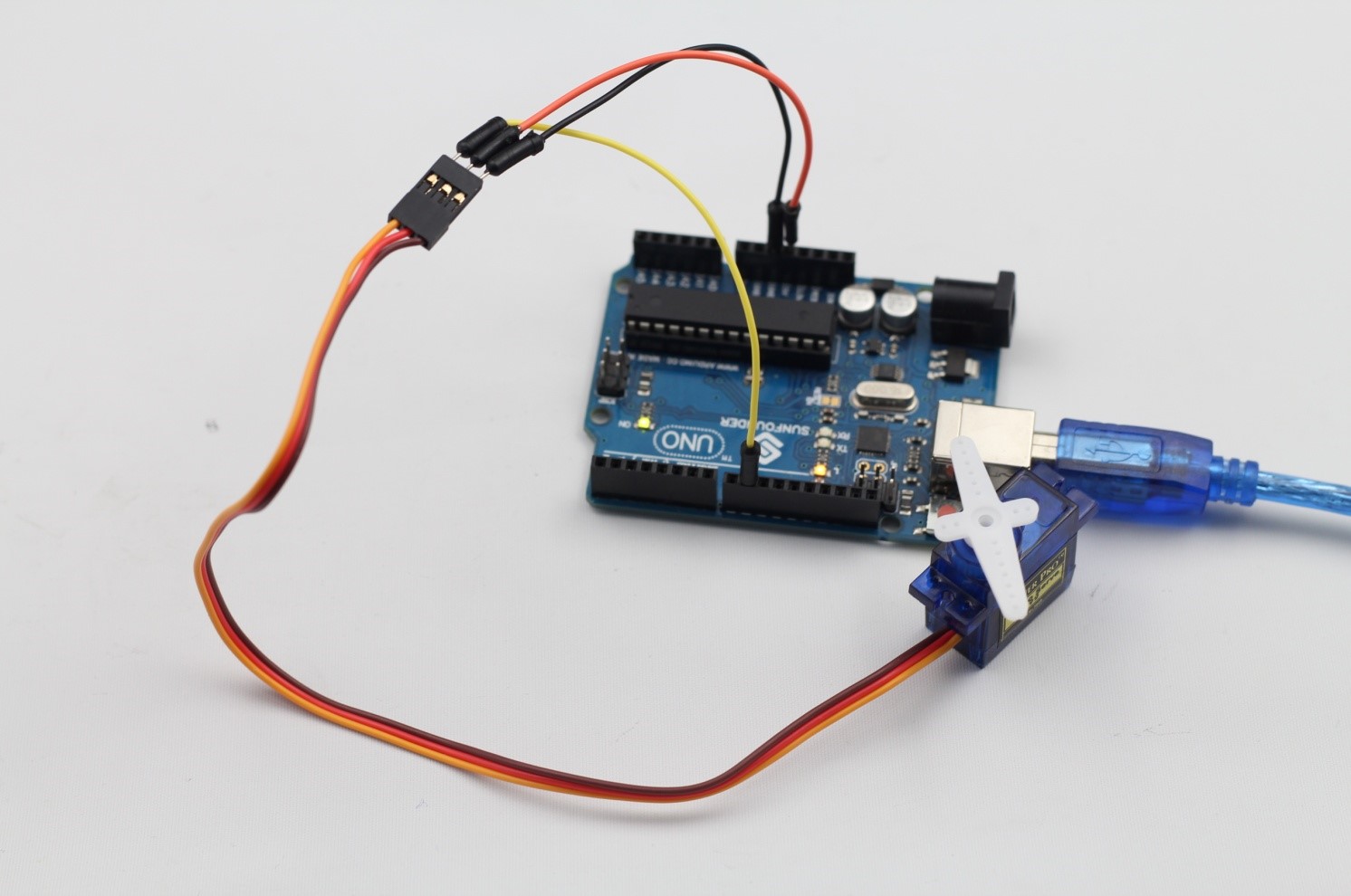
A servo has three wires: the brown wire is GND, the red one is VCC, and the orange one is signal line.

Components
– 1* SunFounder Uno board
– 1 * USB data cable
– 1 * Servo
– Several jumper wires(M to M)
Experimental Principle
Servo
A servo is generally composed of the following parts: case, shaft, gear train, adjustable potentiometer, DC motor, and control circuit board.
It works like this: The SunFounder Uno board sends out PWM signals to the servo, and then the control circuit in the servo receives the signals through the signal pin and controls the motor inside to turn. As a result, the motor drives the gear chain and then motivates the shaft after deceleration. The shaft and adjustable potentiometer of the servo are connected together. When the shaft rotates, it drives the pot, so the pot outputs a voltage signal to the circuit board. Then the board determines the direction and speed of rotation based on the current position, so it can stop exactly at the right position as defined and hold there.
Experimental Procedures
Step 1: Build the circuit
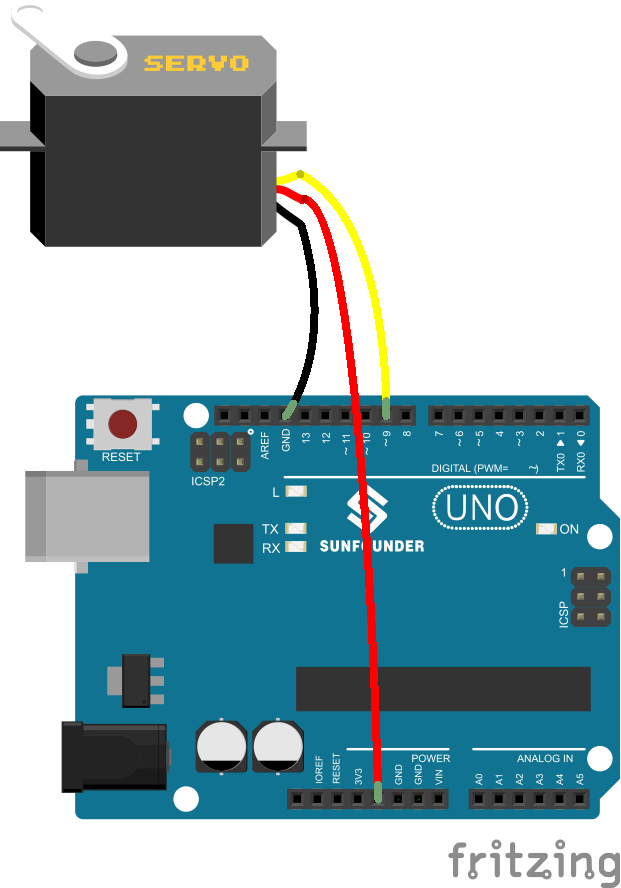
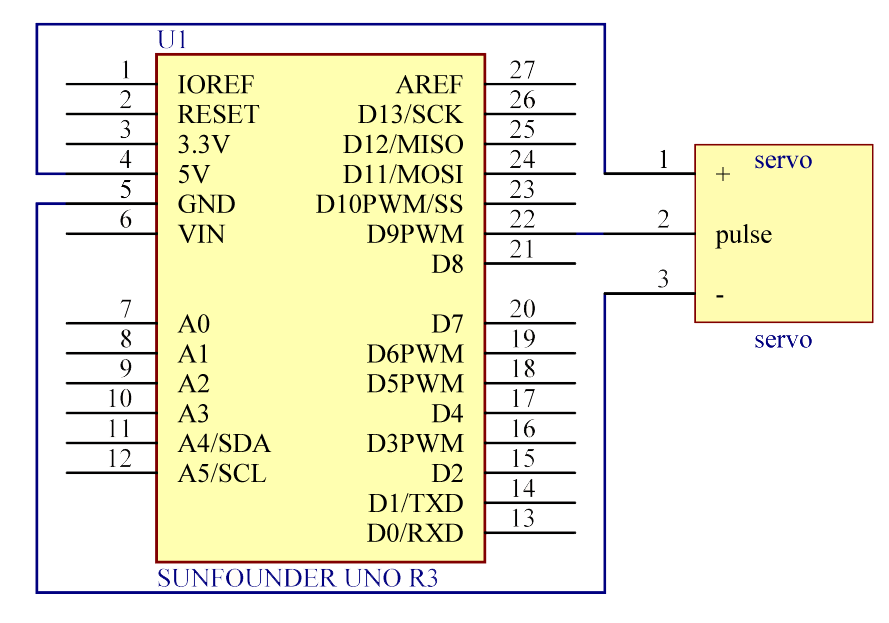
The schematic diagram
Step 2: Program (Please refer to the example code in LEARN -> Get Tutorials on our website)
Step 3: Compile the code.
Step 4: Upload the sketch to the SunFounder Uno board
Now, you can see the rocker arm of the servo rotate and stop at 90 degrees (15 degrees each time). And then it rotates in the opposite direction.
Code
| /*********************************************** * name:Servo * function:you can see the servo motor rotate 90 degrees (rotate once every 15 degrees). * And then rotate in the opposite direction. ************************************************/ //Email: support@sunfounder.com //Website: www.sunfounder.com#include <Servo.h> /************************************************/ Servo myservo;//create servo object to control a servo /************************************************/ void setup() { myservo.attach(9);//attachs the servo on pin 9 to servo object myservo.write(0);//back to 0 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second } /*************************************************/ void loop() { myservo.write(15);//goes to 15 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second myservo.write(30);//goes to 30 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(45);//goes to 45 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(60);//goes to 60 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(75);//goes to 75 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(90);//goes to 90 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second myservo.write(75);//back to 75 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(60);//back to 60 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(45);//back to 45 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(30);//back to 30 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second.33 myservo.write(15);//back to 15 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second myservo.write(0);//back to 0 degrees delay(1000);//wait for a second } /**************************************************/ |
Video
