Introduction
The MPU-6050 is the world’s first and only 6-axis motion tracking devices designed for the low power, low cost, and high performance requirements of smartphones, tablets and wearable sensors.

Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * MPU-6050 module
– 4 * Jumper wires (M to F) (preferable to the 4-pin anti-reverse cable)
Experimental Principle
In this experiment, use I2C to obtain the values of the three-axis acceleration sensor and three-axis gyroscope for MPU6050 and display them on the screen.
Experimental Procedures
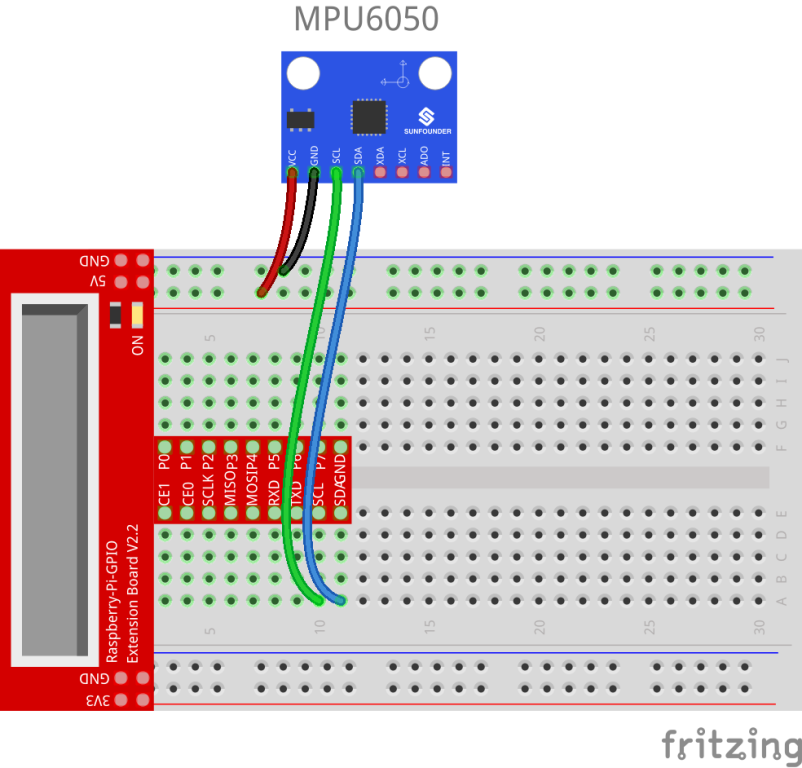
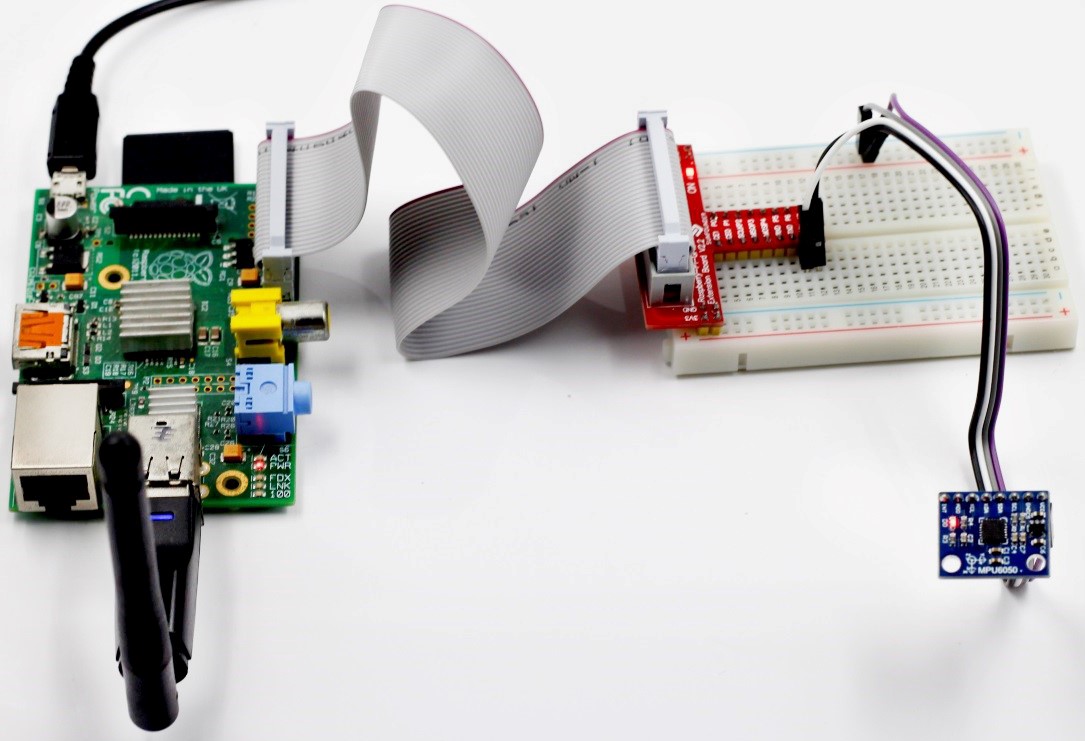
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | MPU-6050 Module |
| SCL | SCL |
| SDA | SDA |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
Step 2: Setup I2C (see Appendix 1. If you have set I2C, skip this step.)
For C language users:
Step 3: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/32_mpu6050/
Step 4: Compile
gcc 32_mpu6050_accel.c –lwiringPi –lm
gcc 32_mpu6050_gyro.c –lwiringPi –lm
Step 5: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 3: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 4: Run
sudo python 32_mpu6050.py
Now you can see the values of the acceleration sensor, gyroscope, and XY-axis rotation read by MPU6050 printed on the screen constantly.
C Code
#include <wiringPiI2C.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int fd;
int acclX, acclY, acclZ;
int gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ;
double acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled;
double gyroX_scaled, gyroY_scaled, gyroZ_scaled;
int read_word_2c(int addr)
{
int val;
val = wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr);
val = val << 8;
val += wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr+1);
if (val >= 0x8000)
val = -(65536 - val);
return val;
}
double dist(double a, double b)
{
return sqrt((a*a) + (b*b));
}
double get_y_rotation(double x, double y, double z)
{
double radians;
radians = atan2(x, dist(y, z));
return -(radians * (180.0 / M_PI));
}
double get_x_rotation(double x, double y, double z)
{
double radians;
radians = atan2(y, dist(x, z));
return (radians * (180.0 / M_PI));
}
int main()
{
fd = wiringPiI2CSetup (0x68);
wiringPiI2CWriteReg8 (fd,0x6B,0x00);//disable sleep mode
printf("set 0x6B=%X\n",wiringPiI2CReadReg8 (fd,0x6B));
while(1) {
acclX = read_word_2c(0x3B);
acclY = read_word_2c(0x3D);
acclZ = read_word_2c(0x3F);
acclX_scaled = acclX / 16384.0;
acclY_scaled = acclY / 16384.0;
acclZ_scaled = acclZ / 16384.0;
printf("My acclX_scaled: %f\n", acclX_scaled);
printf("My acclY_scaled: %f\n", acclY_scaled);
printf("My acclZ_scaled: %f\n", acclZ_scaled);
printf("My X rotation: %f\n", get_x_rotation(acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled));
printf("My Y rotation: %f\n", get_y_rotation(acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled));
delay(100);
}
return 0;
}#include <wiringPiI2C.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int fd;
int acclX, acclY, acclZ;
int gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ;
double acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled;
double gyroX_scaled, gyroY_scaled, gyroZ_scaled;
int read_word_2c(int addr)
{
int val;
val = wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr);
val = val << 8;
val += wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr+1);
if (val >= 0x8000)
val = -(65536 - val);
return val;
}
int main()
{
fd = wiringPiI2CSetup (0x68);
wiringPiI2CWriteReg8 (fd,0x6B,0x00);//disable sleep mode
printf("set 0x6B=%X\n",wiringPiI2CReadReg8 (fd,0x6B));
while(1) {
gyroX = read_word_2c(0x43);
gyroY = read_word_2c(0x45);
gyroZ = read_word_2c(0x47);
gyroX_scaled = gyroX / 131.0;
gyroY_scaled = gyroY / 131.0;
gyroZ_scaled = gyroZ / 131.0;
printf("My gyroX_scaled: %f\n", gyroX_scaled);
printf("My gyroY_scaled: %f\n", gyroY_scaled);
printf("My gyroZ_scaled: %f\n", gyroZ_scaled);
delay(100);
}
return 0;
}Python Code
#!/usr/bin/python
import smbus
import math
import time
# Power management registers
power_mgmt_1 = 0x6b
power_mgmt_2 = 0x6c
def read_byte(adr):
return bus.read_byte_data(address, adr)
def read_word(adr):
high = bus.read_byte_data(address, adr)
low = bus.read_byte_data(address, adr+1)
val = (high << 8) + low
return val
def read_word_2c(adr):
val = read_word(adr)
if (val >= 0x8000):
return -((65535 - val) + 1)
else:
return val
def dist(a,b):
return math.sqrt((a*a)+(b*b))
def get_y_rotation(x,y,z):
radians = math.atan2(x, dist(y,z))
return -math.degrees(radians)
def get_x_rotation(x,y,z):
radians = math.atan2(y, dist(x,z))
return math.degrees(radians)
bus = smbus.SMBus(1) # or bus = smbus.SMBus(1) for Revision 2 boards
address = 0x68 # This is the address value read via the i2cdetect command
# Now wake the 6050 up as it starts in sleep mode
bus.write_byte_data(address, power_mgmt_1, 0)
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
gyro_xout = read_word_2c(0x43)
gyro_yout = read_word_2c(0x45)
gyro_zout = read_word_2c(0x47)
print "gyro_xout : ", gyro_xout, " scaled: ", (gyro_xout / 131)
print "gyro_yout : ", gyro_yout, " scaled: ", (gyro_yout / 131)
print "gyro_zout : ", gyro_zout, " scaled: ", (gyro_zout / 131)
accel_xout = read_word_2c(0x3b)
accel_yout = read_word_2c(0x3d)
accel_zout = read_word_2c(0x3f)
accel_xout_scaled = accel_xout / 16384.0
accel_yout_scaled = accel_yout / 16384.0
accel_zout_scaled = accel_zout / 16384.0
print "accel_xout: ", accel_xout, " scaled: ", accel_xout_scaled
print "accel_yout: ", accel_yout, " scaled: ", accel_yout_scaled
print "accel_zout: ", accel_zout, " scaled: ", accel_zout_scaled
print "x rotation: " , get_x_rotation(accel_xout_scaled, accel_yout_scaled, accel_zout_scaled)
print "y rotation: " , get_y_rotation(accel_xout_scaled, accel_yout_scaled, accel_zout_scaled)
time.sleep(0.5)
