Introduction
Temperature Sensor DS18B20 is a commonly used digital temperature sensor featured with small size, low-cost hardware, strong anti-interference capability and high precision. The digital temperature sensor is easy to wire and can be applied a various occasions after packaging. Different from conventional AD collection temperature sensors, it uses a 1-wire bus and can directly output temperature data.
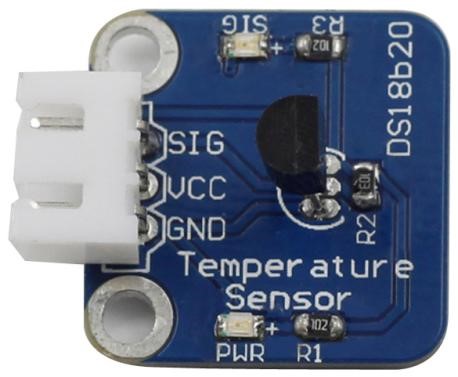
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * DS18B20 Temperature Sensor module
– 1 * 3-Pin Anti-reverse Cable
Experimental Principle
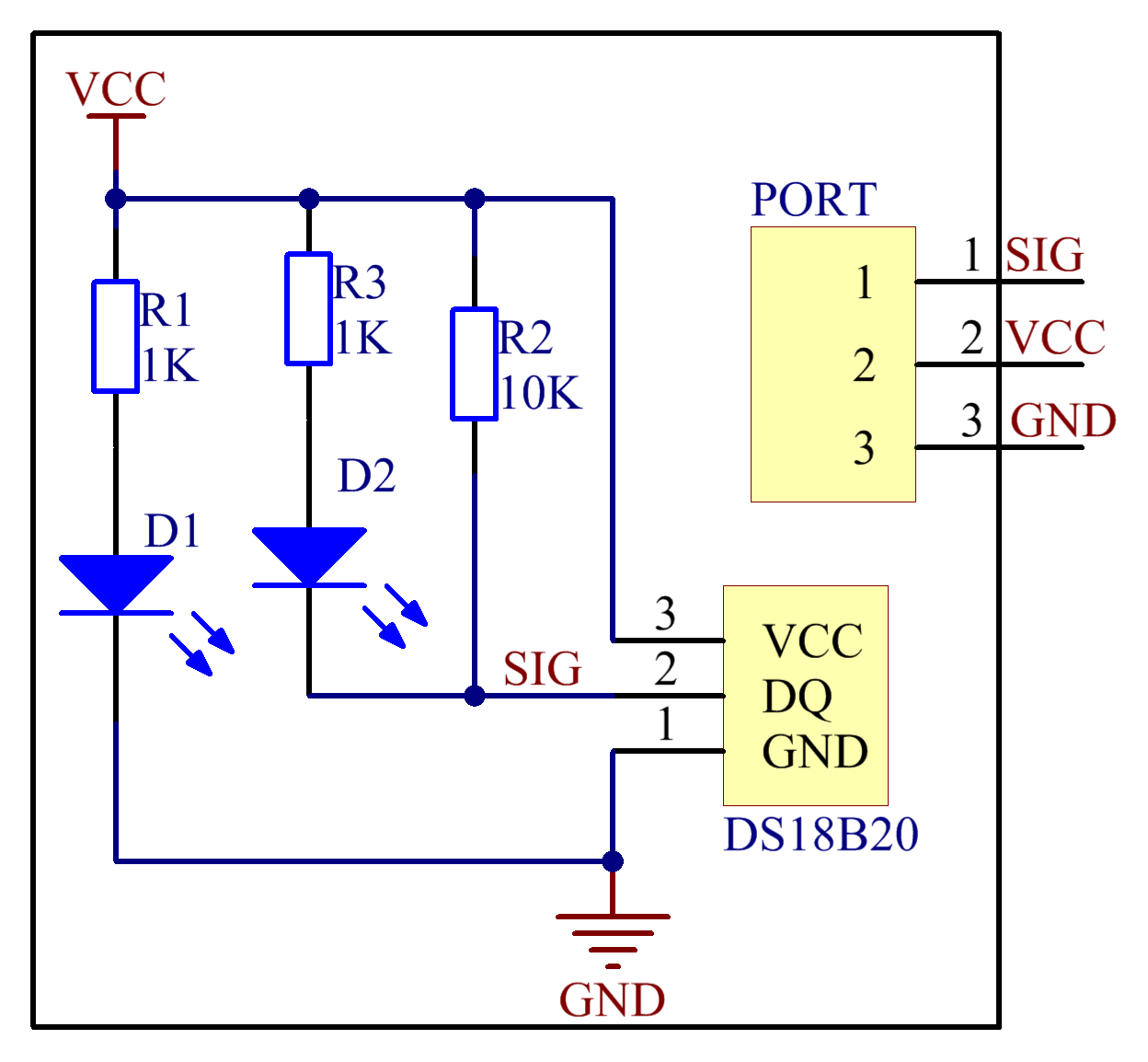
With a unique single-wire interface, DS18B20 requires only one pin for a two-way communication with a microprocessor. It supports multi-point networking to measure multi-point temperatures. Eight sensors can be connected at most, because it will consume too much power supply and cause low voltage thus harming the stability of transmission.
When using the DS18B20, you need to connect a 10KΩ resistor to the middle pin DQ to pull up the level.
The schematic diagram:
Experimental Procedures
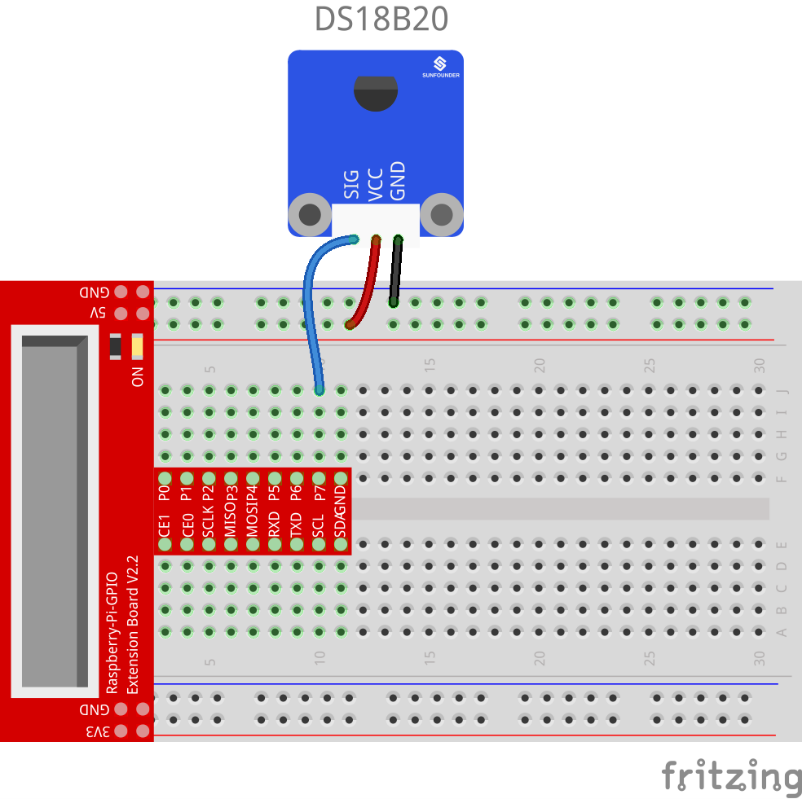
Step 1:Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | DS18B20 Temperature Sensor |
| GPIO7 | SIG |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
Step 2:Upgrade your kernel
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
Step 3:You can edit that file with nano
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Then scroll to the bottom and type
dtoverlay=w1-gpio
Then reboot with
sudo reboot.
Mount the device drivers and confirm whether the device is effective or not
sudo modprobe w1-gpio
sudo modprobe w1-therm
cd /sys/bus/w1/devices/
ls
The result is as follows:
root@rasberrypi:/sys/bus/w1/devices# ls
28-00000495db35 w1_bus_master1
28-00000495db35 is an external temperature sensor device, but it may vary with every client. This is the serial number of your ds18b20.
Step 4:Check the current temperature
cd 28-00000495db35
ls
The result is as follows:
root@rasberrypi:/sys/bus/w1/devices/28-00000495db35# ls
driver id name power subsystem uevent w1_slave
cat w1_slave
The result is as follows:
root@raspberrypi:/sys/bus/w1_slave/28-00000495db35# cat w1_slave
a3 01 4b 46 7f ff 0d 10 ce : crc=ce YES
a3 01 4b 46 7f ff 0d 10 ce t=26187
The second line t=26187 is current temperature value. If you want to convert it to degree Celsius, you can divide by 1000, that is, the current temperature is 26187/1000=26.187 ℃.
For C language users:
Step 2: Change directory and edit
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/26_ds18b20/
nano ds18b20.c
Find the following line, replace “28-031467805fff” with your sensor address. Save and exit.
char* addr = “/sys/bus/w1/devices/28-031467805fff/w1_slave”;
Step 6:Compile
gcc ds18b20.c
Step 7:Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 5: Change directory and edit
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
nano 26_ds18b20.py
Step 6: Run
sudo python 26_ds18b20.py
Now, you can see the current temperature value displayed on the screen.
C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define BUFSIZE 128
char* addr = "/sys/bus/w1/devices/28-031467805fff/w1_slave";
int main(void)
{
float temp;
int i, j;
int fd;
int ret;
char buf[BUFSIZE];
char tempBuf[5];
while (1){
fd = open(addr, O_RDONLY);
if(-1 == fd){
perror("open device file error");
return 1;
}
while(1){
ret = read(fd, buf, BUFSIZE);
if(0 == ret){
break;
}
if(-1 == ret){
if(errno == EINTR){
continue;
}
perror("read()");
close(fd);
return 1;
}
}
for(i=0;i<sizeof(buf);i++){
if(buf[i] == 't'){
for(j=0;j<sizeof(tempBuf);j++){
tempBuf[j] = buf[i+2+j];
}
}
}
temp = (float)atoi(tempBuf) / 1000;
printf("%.3f C\n",temp);
close(fd);
}
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
#----------------------------------------------------------------
# Note:
# ds18b20's data pin must be connected to pin7.
# replace the 28-XXXXXXXXX as yours.
#----------------------------------------------------------------
import os
ds18b20 = ''
def setup():
global ds18b20
for i in os.listdir('/sys/bus/w1/devices'):
if i != 'w1_bus_master1':
ds18b20 = i
def read():
# global ds18b20
location = '/sys/bus/w1/devices/' + ds18b20 + '/w1_slave'
tfile = open(location)
text = tfile.read()
tfile.close()
secondline = text.split("\n")[1]
temperaturedata = secondline.split(" ")[9]
temperature = float(temperaturedata[2:])
temperature = temperature / 1000
return temperature
def loop():
while True:
if read() != None:
print "Current temperature : %0.3f C" % read()
def destroy():
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
setup()
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
