Introduction
A touch sensor operate with the conductivity of human body. When you touch the metal on the base electrode of the transistor, the level of pin SIG will turn over.

Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * Touch Switch module
– 1 * Dual-Color LED module
– 2 * 3-Pin anti-reverse cable
Experimental Principle
In this experiment, touch the base electrode of the transistor by fingers to make it conduct as human body itself is a kind of conductor and an antenna that can receive electromagnetic waves in the air. These electromagnetic wave signals collected from the human body are amplified by the transistor and processed by the comparator on the module to output steady signals. The schematic diagram:
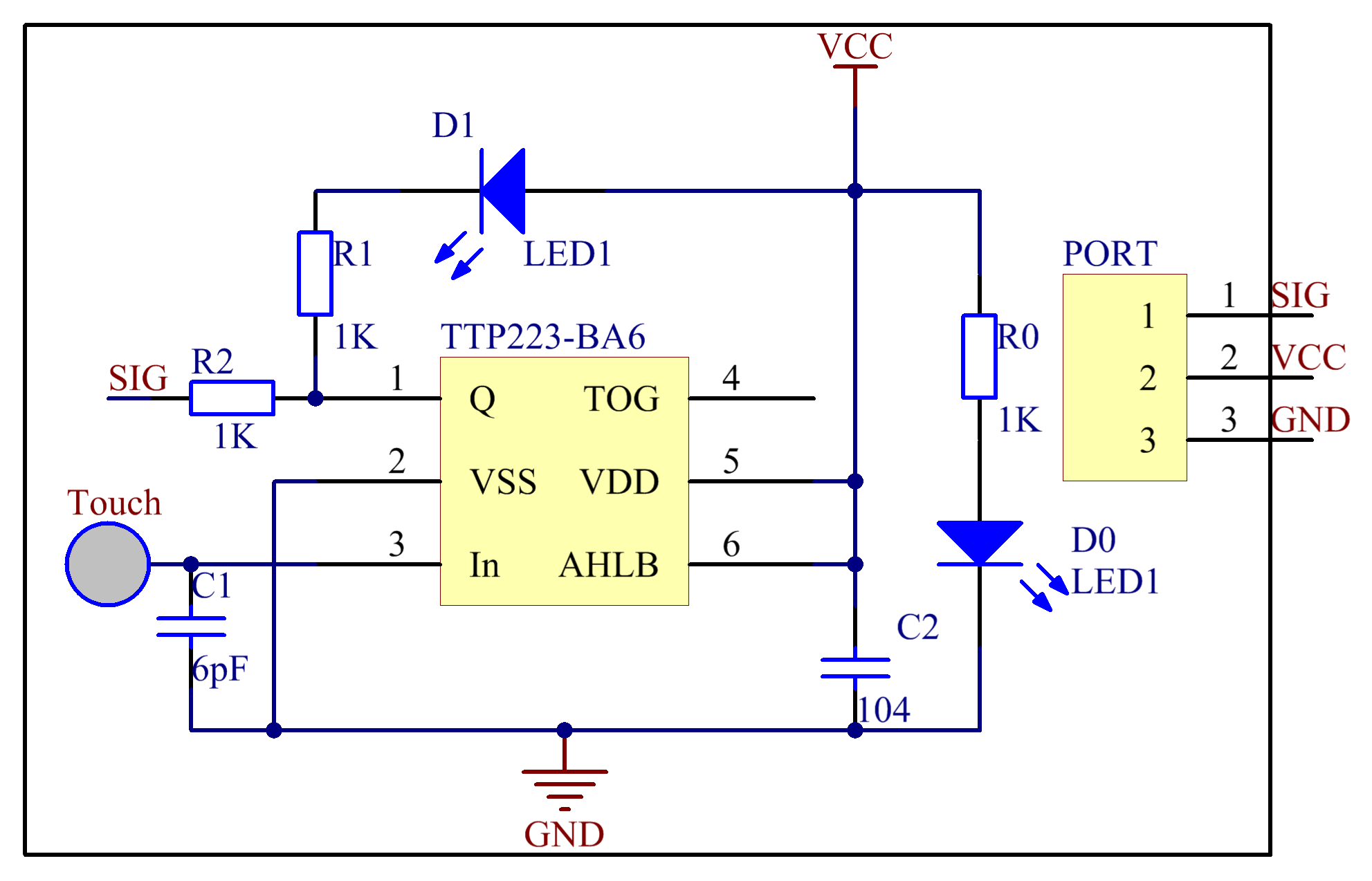
Experimental Procedures
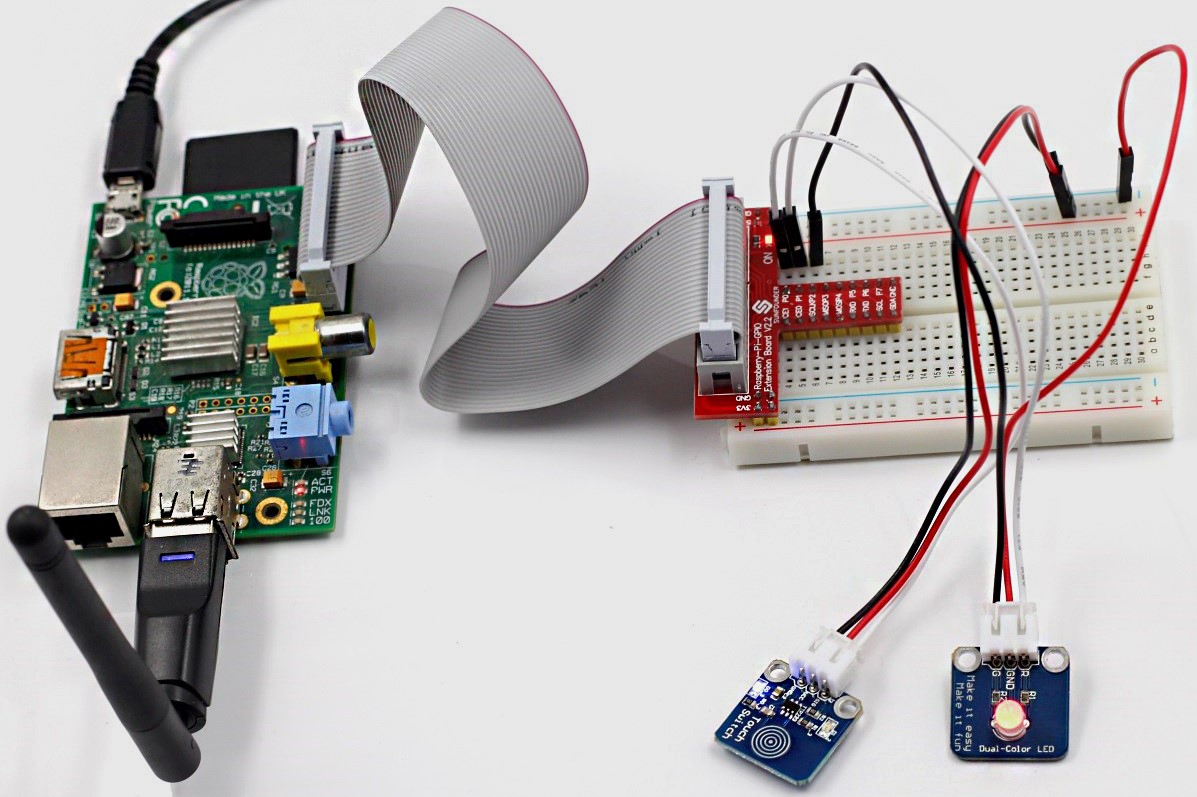
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | Touch Switch Module |
| GPIO0 | SIG |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| Raspberry Pi | Dual-Color LED Module |
| GPIO1 | R |
| GND | GND |
| GPIO2 | G |
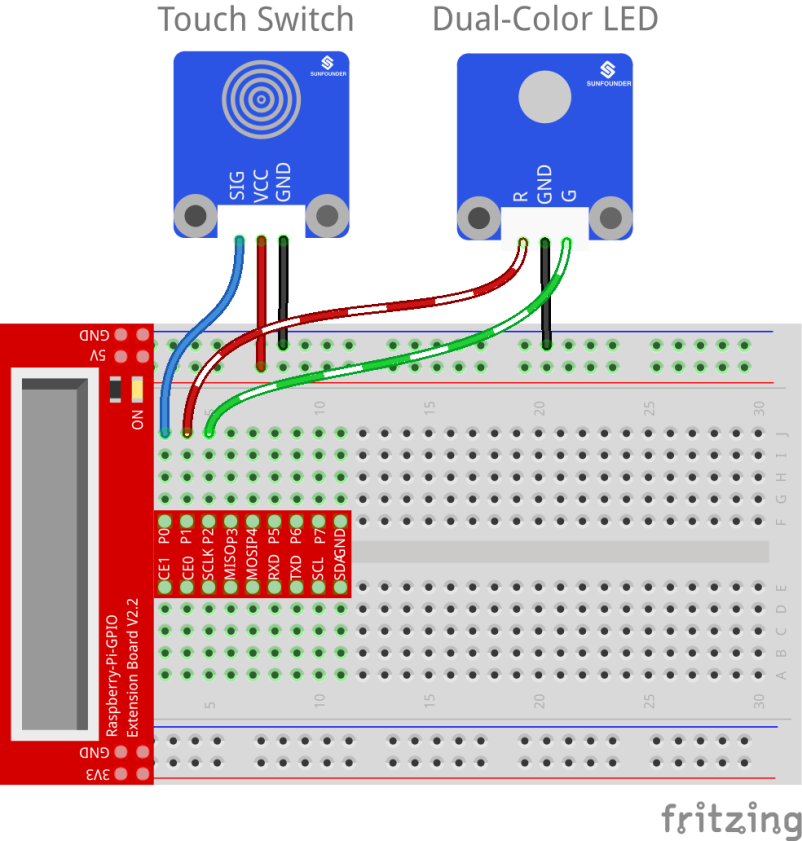
For C language users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/24_touch_switch/
Step 3: Compile
gcc touch_switch.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 3: Run
sudo python 24_touch_switch.py
Now, touch the metal disk, you can see the LED change its colors and “ON” and “OFF” printed on the screen.
C Code
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define TouchPin 0
#define Gpin 1
#define Rpin 2
int tmp = 0;
void LED(int color)
{
pinMode(Gpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Rpin, OUTPUT);
if (color == 0)
{
digitalWrite(Rpin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(Gpin, LOW);
}
else if (color == 1)
{
digitalWrite(Rpin, LOW);
digitalWrite(Gpin, HIGH);
}
else
printf("LED Error");
}
void Print(int x){
if (x != tmp){
if (x == 0)
printf("...ON\n");
if (x == 1)
printf("OFF..\n");
tmp = x;
}
}
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print messageto screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
pinMode(TouchPin, INPUT);
while(1){
LED(digitalRead(TouchPin));
Print(digitalRead(TouchPin));
}
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
TouchPin = 11
Gpin = 12
Rpin = 13
tmp = 0
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(Gpin, GPIO.OUT) # Set Green Led Pin mode to output
GPIO.setup(Rpin, GPIO.OUT) # Set Red Led Pin mode to output
GPIO.setup(TouchPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Set BtnPin's mode is input, and pull up to high level(3.3V)
def Led(x):
if x == 0:
GPIO.output(Rpin, 1)
GPIO.output(Gpin, 0)
if x == 1:
GPIO.output(Rpin, 0)
GPIO.output(Gpin, 1)
def Print(x):
global tmp
if x != tmp:
if x == 0:
print ' **********'
print ' * ON *'
print ' **********'
if x == 1:
print ' **********'
print ' * OFF *'
print ' **********'
tmp = x
def loop():
while True:
Led(GPIO.input(TouchPin))
Print(GPIO.input(TouchPin))
def destroy():
GPIO.output(Gpin, GPIO.HIGH) # Green led off
GPIO.output(Rpin, GPIO.HIGH) # Red led off
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
