Introduction
An infrared-receiver is a component that receives infrared signals and can independently receive infrared ray and output signals compatible with TTL level. It’s similar with a normal plastic-packaged transistor in size and it is suitable for all kinds of infrared remote control and infrared transmission.
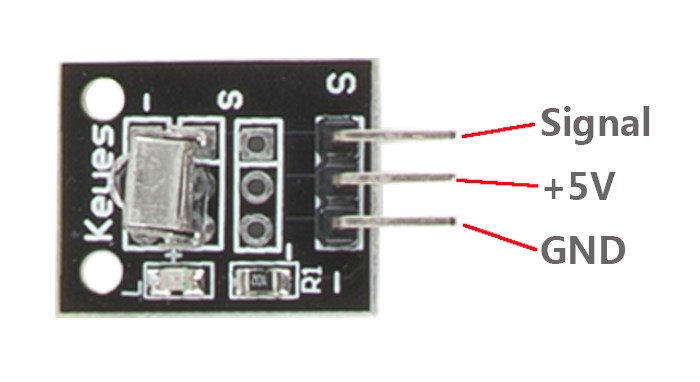
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * Infrared-receiver module
– Several jumper wires
Experimental Principle
Infrared receiving head receives infrared signals.
Experimental Procedures
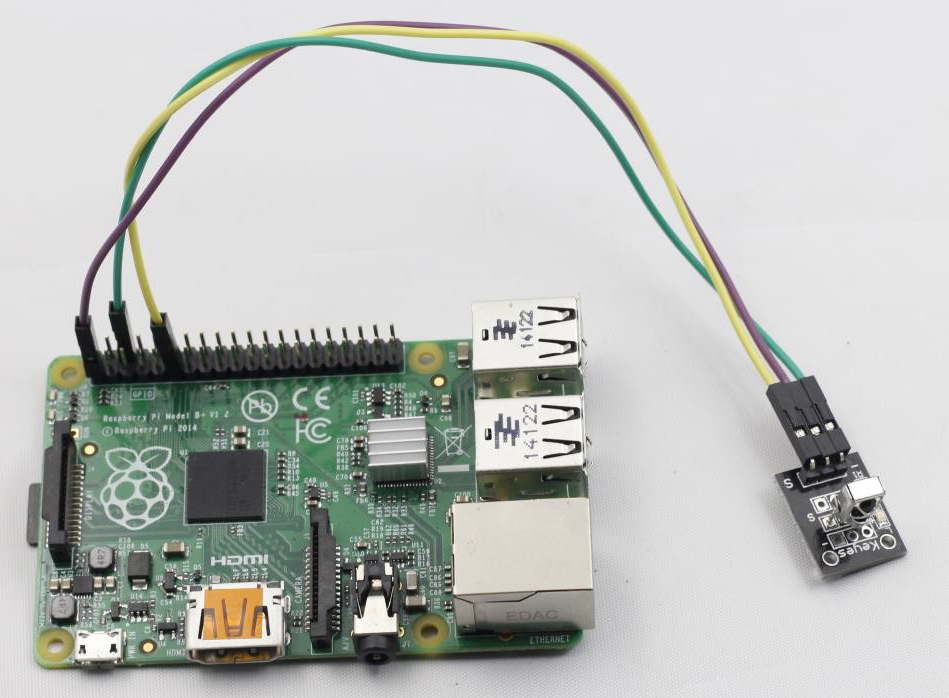
Step 1: Build the circuit
Infrared-Receiver Module Raspberry Pi
S ———————————————- GPIO0
+ ———————————————- 3.3V
– ———————————————– GND
Step 2: Edit and save the code (see path/Rpi_SensorKit_code/29_irRecv/irRecv.c)
Step 3: Compile
gcc irRecv.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
./a.out
Here you can see the LED on the module light up when infrared rays are received. At the same time, infrared pulses will be printed on the screen.

irRecv.c
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define IR 0
int cnt = 0;
void myISR(void)
{
printf("Recevied infrared. cnt = %d\n", ++cnt);
}
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print messageto screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
if(wiringPiISR(IR, INT_EDGE_FALLING, &myISR) == -1){
printf("setup ISR failed !");
return 1;
}
//pinMode(IR, INPUT);
while(1);
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
IrPin = 11
LedPin = 12
Led_status = 1
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set LedPin's mode is output
GPIO.setup(IrPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set LedPin high(+3.3V) to off led
def swLed(ev=None):
global Led_status
Led_status = not Led_status
GPIO.output(LedPin, Led_status) # switch led status(on-->off; off-->on)
if Led_status == 1:
print 'led on...'
else:
print '...led off'
def loop():
GPIO.add_event_detect(IrPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=swLed) # wait for falling
while True:
pass # Don't do anything
def destroy():
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # led off
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()