Introduction
In this lesson, we will learn how to use the acceleration sensor ADXL345.
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * ADXL345 module
– Jumper wires
Principle
ADXL345
The ADXL345 is a small, thin, low power, 3-axis accelerometer with high resolution (13-bit) measurement at up to ±16 g. Digital output data is formatted as 16-bit two’s complement and is accessible through either an SPI (3- or 4-wire) or I2C digital interface.
The ADXL345 is well suited to measure the static acceleration of gravity in tilt-sensing applications, as well as dynamic acceleration resulting from motion or shock. Its high resolution (4 mg/LSB) enables the inclination change measurement by less than 1.0°. And the excellent sensitivity (3.9mg/LSB @2g) provides a high-precision output of up to ±16g. In this experiment, I2C digital interface is used.
Experimental Procedures
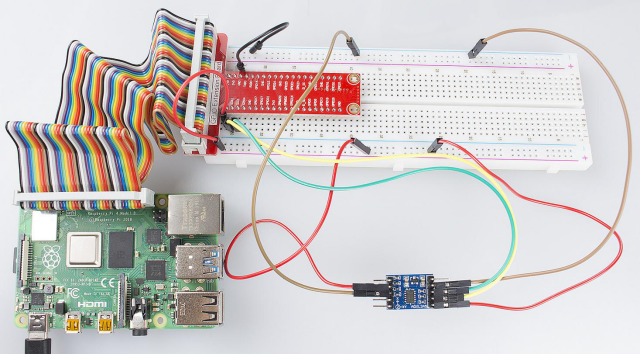
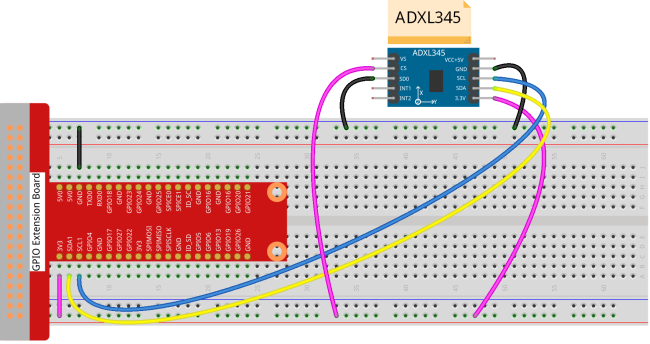
Step 1: Build the circuit.
ADXL345 Module Raspberry Pi
GND ————————– GND
3.3V ————————– 3.3V
SCL ————————— SCL1
SDA ————————– SDA1
CS —————————- 3.3V
SDO ————————– GND
The I2C interface is used in the following program. Before running the program, please make sure the I2C driver module of Raspberry Pi has loaded normally(Refer to Appendix).
For C Language Users:
Step 2: Change directory.
cd /home/pi/Sunfounder_SuperKit_C_code_for_RaspberryPi/14_ADXL345/Step 3: Compile.
gcc adxl345.c -o adxl345 -lwiringPiStep 4: Run.
sudo ./adxl345For Python Users:
Step 2: Change directory.
cd /home/pi/Sunfounder_SuperKit_Python_code_for_RaspberryPiStep 3: Run.
sudo python3 14_ADXL345.py Now, rotate the acceleration sensor, and you should see the values printed on the screen change.