Introduction
The rain detection module detects rain on the board. Place the rain detection board in the open air. When it is raining, the rain detection module will sense the raindrops and send signals to the Raspberry Pi.
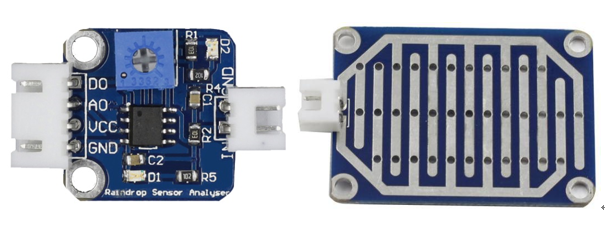
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * Rain Detection module
– 1 * PCF8591
– 1 * LM393
– 1 * 2-Pin ribbon cable
– 1 * 4-Pin anti-reverse cable
– Several jumper wires (M to F)
– 1 * Glass of water (Self provided)
Experimental Principle
There are two metal wires that are close to each other but do not cross on the rain detection board. When rain drops on the board, the two metal wires will conduct, thus there is a voltage between the two metal wires. The schematic diagram is as shown below:
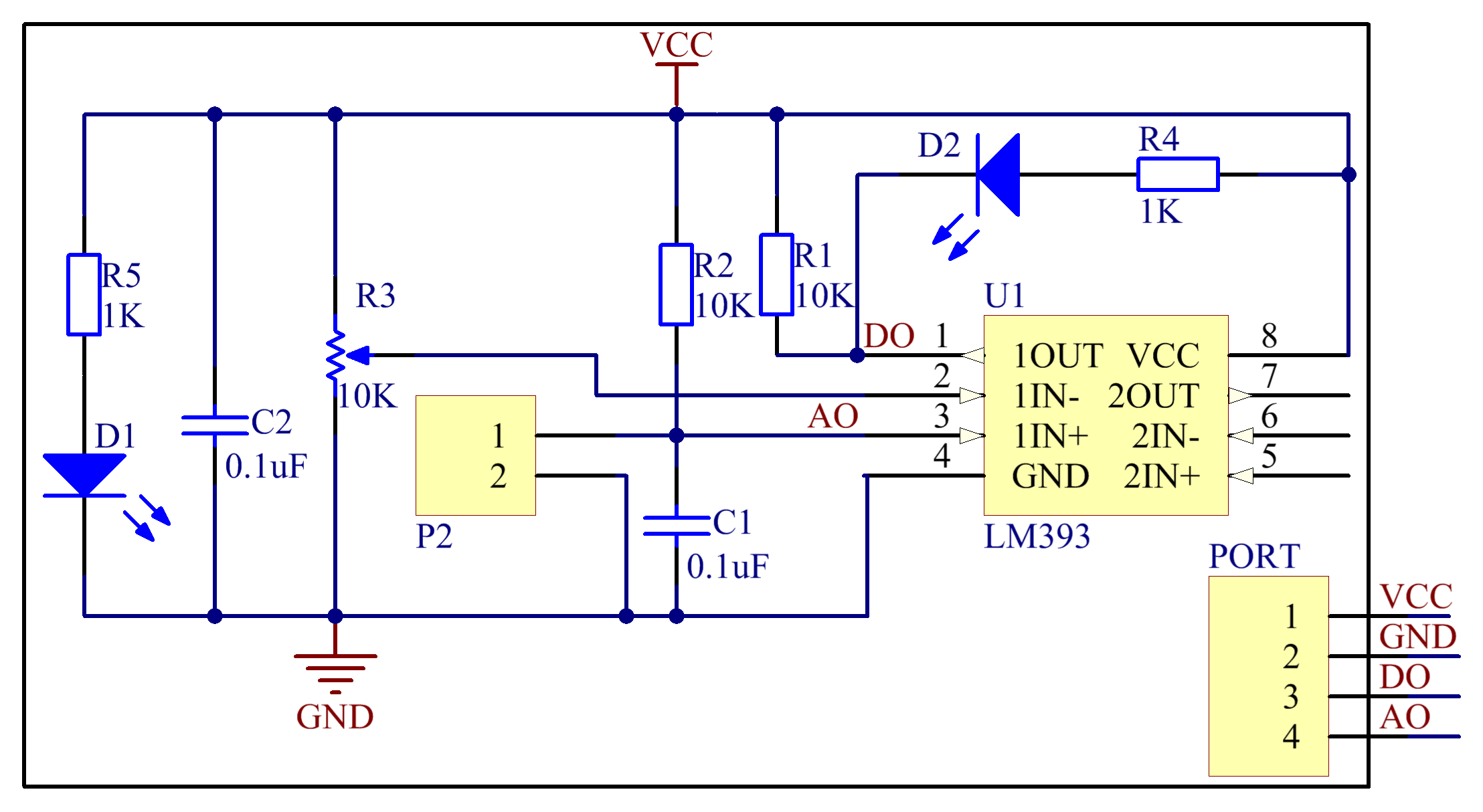
Experimental Procedures
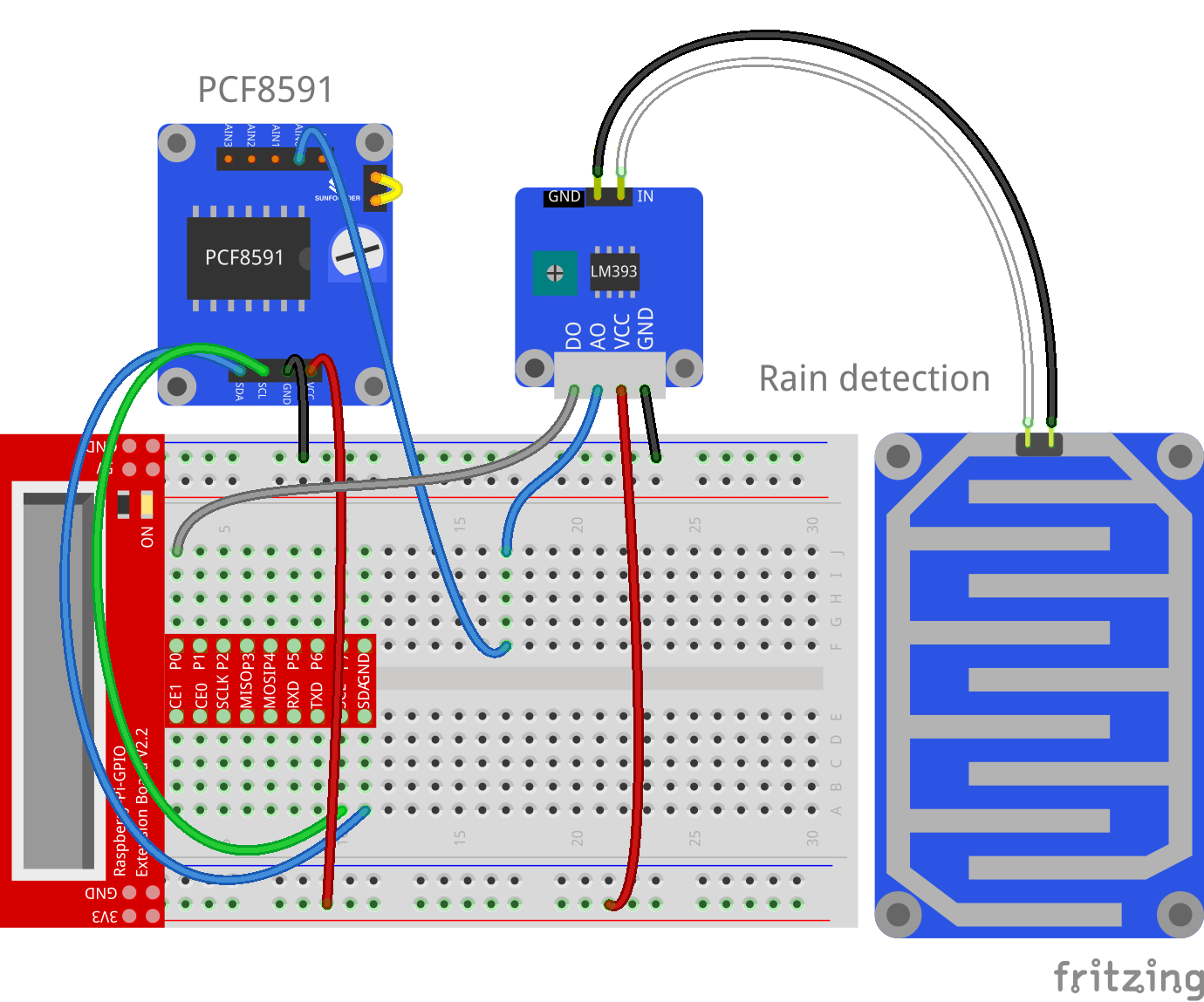
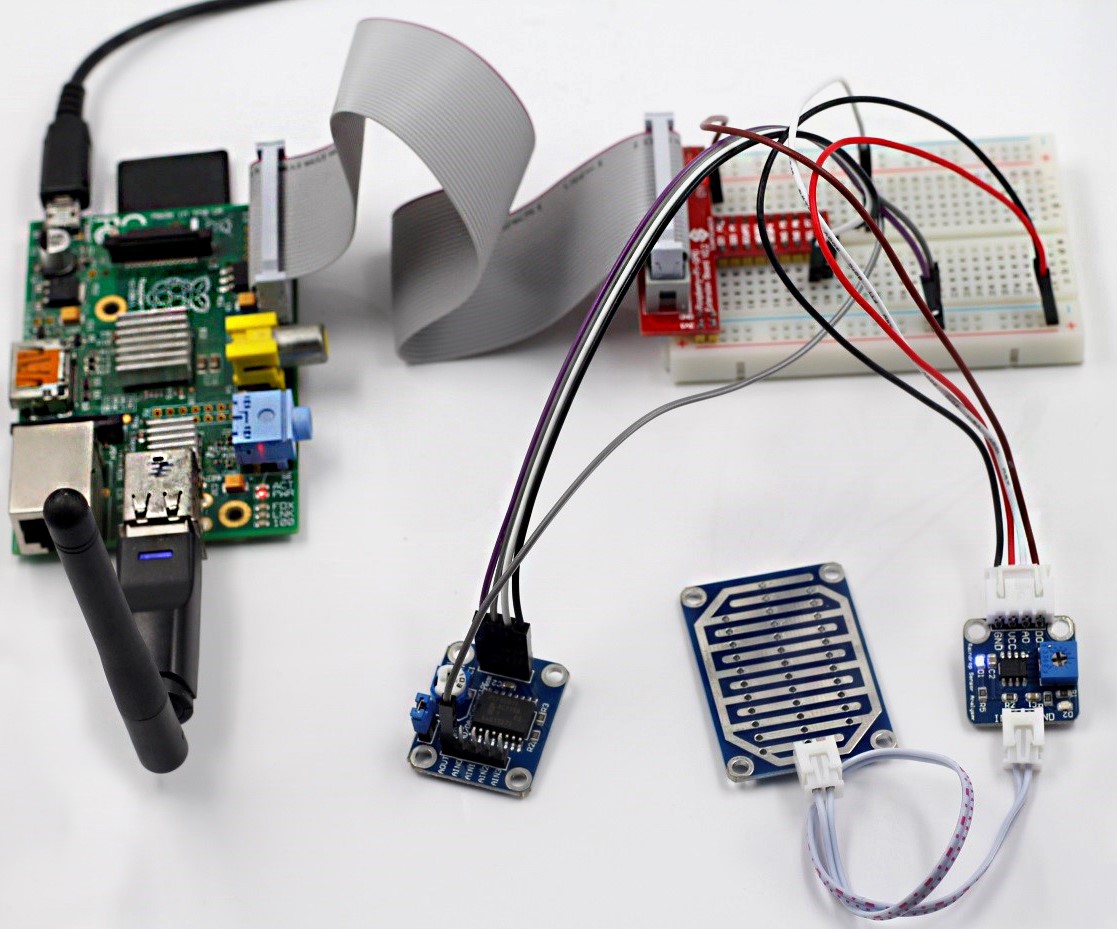
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | PCF8591 Module | LM393 |
| SDA | SDA | * |
| SCL | SCL | * |
| 3V3 | VCC | VCC |
| GND | GND | GND |
| GPIO0 | * | DO |
| * | AIN0 | AO |
| Rain Detection Board | LM393 |
| – | IN |
| – | GND |
Note:The two pins on the rain detection board are exactly the same. You can connect them to pin IN and GND on LM393.
For C language users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/14_rain_detector/
Step 3: Compile
gcc rain_detector.c –lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 3: Run
sudo python 14_rain_detector.py
Now dip some water onto the rain detection board until “raining” display on the screen. You can adjust the potentiometer on LM393 to detect the threshold of rainfall.
C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <pcf8591.h>
#include <math.h>
#define PCF 120
#define DOpin 0
void Print(int x)
{
switch(x)
{
case 1:
printf("\n***************\n" );
printf( "* Not Raining *\n" );
printf( "***************\n\n");
break;
case 0:
printf("\n*************\n" );
printf( "* Raining!! *\n" );
printf( "*************\n\n");
break;
default:
printf("\n**********************\n" );
printf( "* Print value error. *\n" );
printf( "**********************\n\n");
break;
}
}
int main()
{
int analogVal;
int tmp, status;
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
// Setup pcf8591 on base pin 120, and address 0x48
pcf8591Setup(PCF, 0x48);
pinMode(DOpin, INPUT);
status = 0;
while(1) // loop forever
{
analogVal = analogRead(PCF + 0);
printf("%d\n", analogVal);
tmp = digitalRead(DOpin);
if (tmp != status)
{
Print(tmp);
status = tmp;
}
delay (200);
}
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
import PCF8591 as ADC
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import math
DO = 17
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
def setup():
ADC.setup(0x48)
GPIO.setup(DO, GPIO.IN)
def Print(x):
if x == 1:
print ''
print ' ***************'
print ' * Not raining *'
print ' ***************'
print ''
if x == 0:
print ''
print ' *************'
print ' * Raining!! *'
print ' *************'
print ''
def loop():
status = 1
while True:
print ADC.read(0)
tmp = GPIO.input(DO);
if tmp != status:
Print(tmp)
status = tmp
time.sleep(0.2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
setup()
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
