Introduction
There are five operation directions for joystick PS2: up, down, left, right and press-down.
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * PCF8591
– 1 * Joystick PS2 module
– 1 * 5-Pin anti-reverse cable
– Several Jumper wires (M to F)
Experimental Principle
This module has two analog outputs (corresponding to X and Y coordinates) and one digital output representing whether it is pressed on Z axis.
In this experiment, we connect pin X and Y to the analog input ports of the A/D convertor so as to convert analog quantities into digital ones. Then program on Raspberry Pi to detect the moving direction of the Joystick.
The schematic diagram:
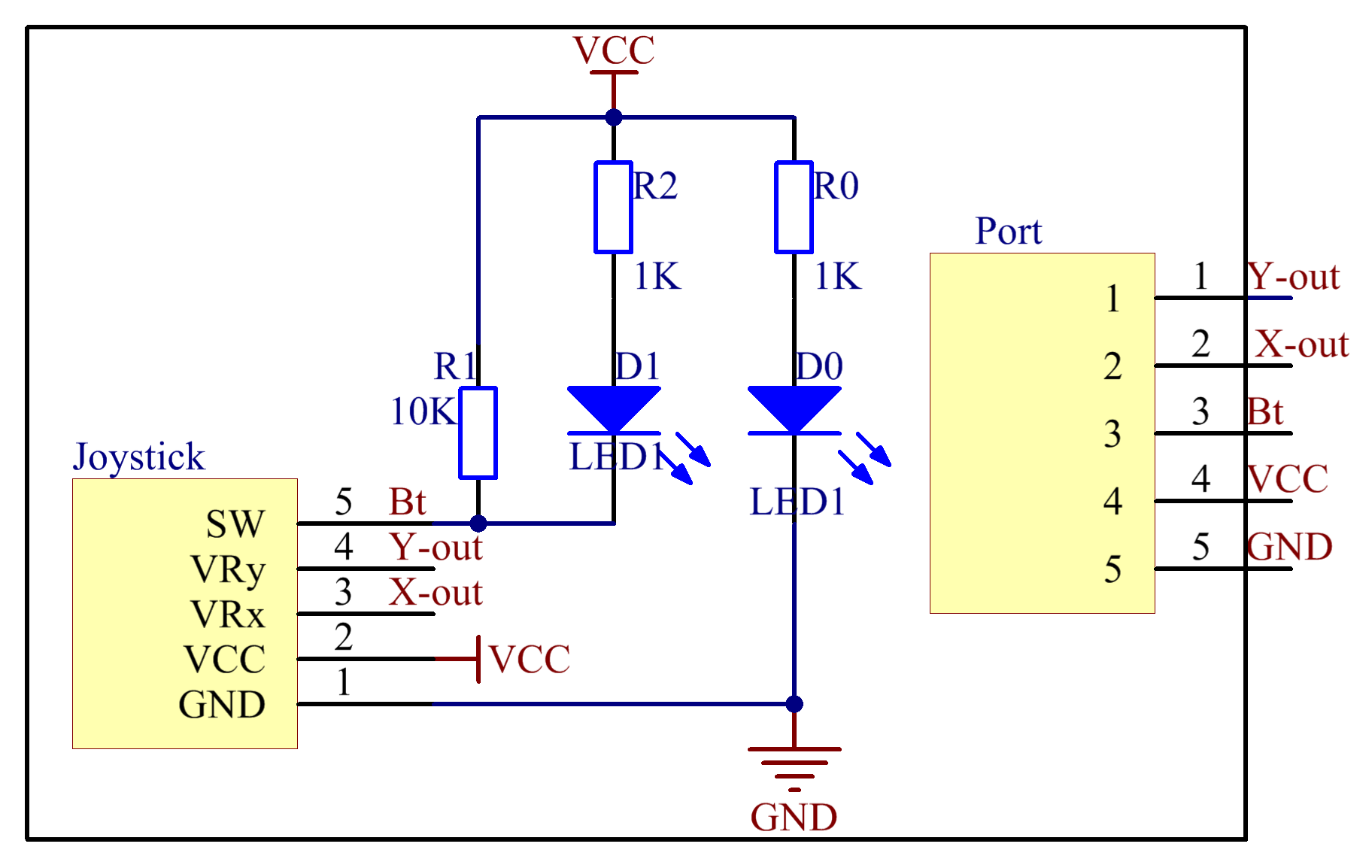
Experimental Procedures
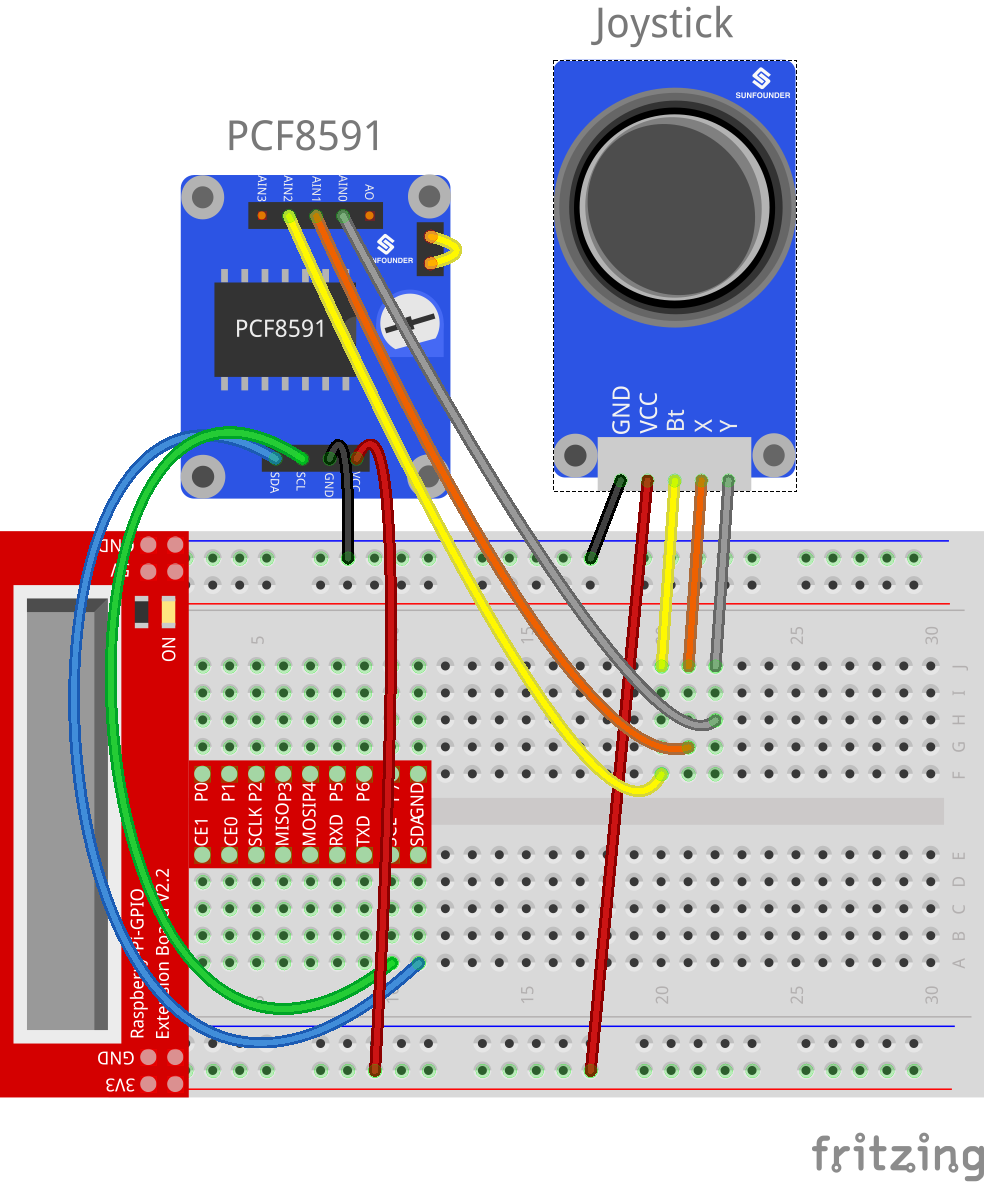
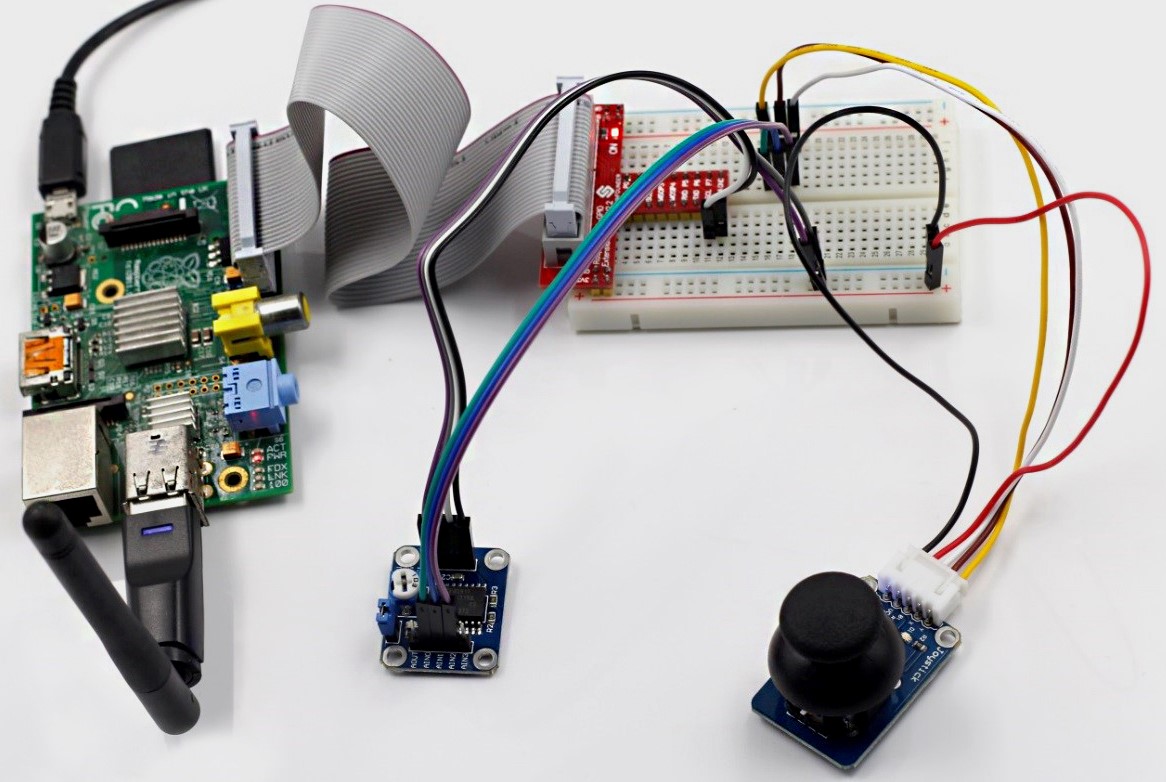
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | PCF8591 Module | Joystick PS2 |
| SDA | SDA | |
| SCL | SCL | |
| 3.3V | VCC | VCC |
| GND | GND | GND |
| * | AIN0 | Y |
| * | AIN1 | X |
| * | AIN2 | Bt |
For C language users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/15_joystick_PS2/
Step 3: Compile
gcc joystick_PS2.c –lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 3: Run
sudo python 15_joystick_PS2.py
Now push the rocker upwards, and a string “up” will be printed on the screen; push it downwards, and “down” will be printed; if you push it left, “Left” will be printed on; If you push it right, and “Right” will be printed; If you press down the cap, “Button Pressed” will be printed on the screen.
C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <pcf8591.h>
#define PCF 120
#define uchar unsigned char
int AIN0 = PCF + 0;
int AIN1 = PCF + 1;
int AIN2 = PCF + 2;
char *state[6] = {"home", "up", "down", "left", "right", "pressed"};
int direction(){
int x, y, b;
int tmp;
x = analogRead(AIN1);
y = analogRead(AIN0);
b = analogRead(AIN2);
if (y == 0)
tmp = 1; // up
if (y == 255)
tmp = 2; // down
if (x == 255)
tmp = 3; // left
if (x == 0)
tmp = 4; // right
if (b == 0)
tmp = 5; // button preesd
if (x-125<15 && x-125>-15 && y-125<15 && y-125>-15 && b == 255)
tmp = 0; // home position
return tmp;
}
int main (void)
{
int tmp;
int status = 0;
wiringPiSetup ();
// Setup pcf8591 on base pin 120, and address 0x48
pcf8591Setup (PCF, 0x48);
while(1) // loop forever
{
tmp = direction();
if (tmp != status)
{
printf("%s\n", state[tmp]);
status = tmp;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
#------------------------------------------------------
#
# This is a program for JoystickPS2 Module.
#
# This program depend on PCF8591 ADC chip. Follow
# the instruction book to connect the module and
# ADC0832 to your Raspberry Pi.
#
#------------------------------------------------------
import PCF8591 as ADC
import time
def setup():
ADC.setup(0x48) # Setup PCF8591
global state
def direction(): #get joystick result
state = ['home', 'up', 'down', 'left', 'right', 'pressed']
i = 0
if ADC.read(0) <= 5:
i = 1 #up
if ADC.read(0) >= 250:
i = 2 #down
if ADC.read(1) >= 250:
i = 3 #left
if ADC.read(1) <= 5:
i = 4 #right
if ADC.read(2) == 0:
i = 5 # Button pressed
if ADC.read(0) - 125 < 15 and ADC.read(0) - 125 > -15 and ADC.read(1) - 125 < 15 and ADC.read(1) - 125 > -15 and ADC.read(2) == 255:
i = 0
return state[i]
def loop():
status = ''
while True:
tmp = direction()
if tmp != None and tmp != status:
print tmp
status = tmp
def destroy():
pass
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
