Introduction
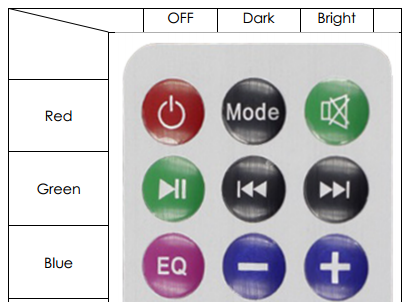
Each button of an IR remote control (as shown below) has a string of specific encoding. When a button is pressed, the IR transmitter in the remote control will send out the corresponding IR encoding signals. On the other side, when the IR receiver receives certain encoding signals, it will decode them to identify which button is pressed.

Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * IR Receiver
– 1 * RGB LED module
– 1 * IR Remote Control
– 1 * 3-Pin anti-reverse cable
– 1 * 4-Pin anti-reverse cable
Experimental Principle
In this experiment, we use the lirc library to read infrared signals returned by buttons of the remote control and translate them to button values. Then use liblircclient-dev (C) and pylirc (Python) to simplify the process for reading values from the remote control. In this experiment use 9 buttons on the top of the remote to control the color of the RGB LED module. Each row represents one color, and each column represents the brightness.
Experimental Procedures
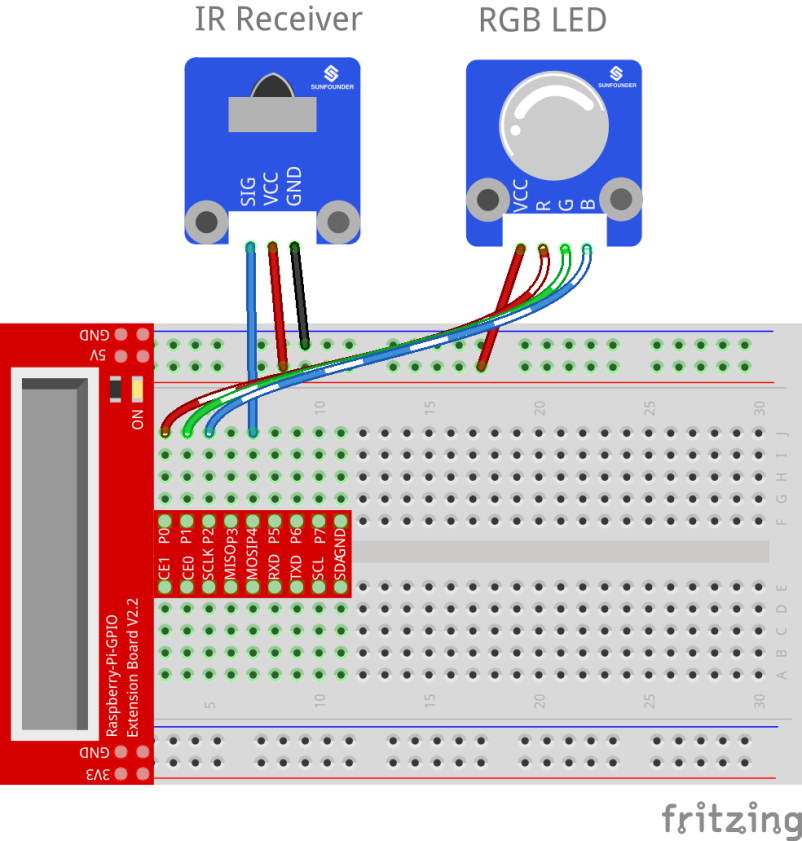
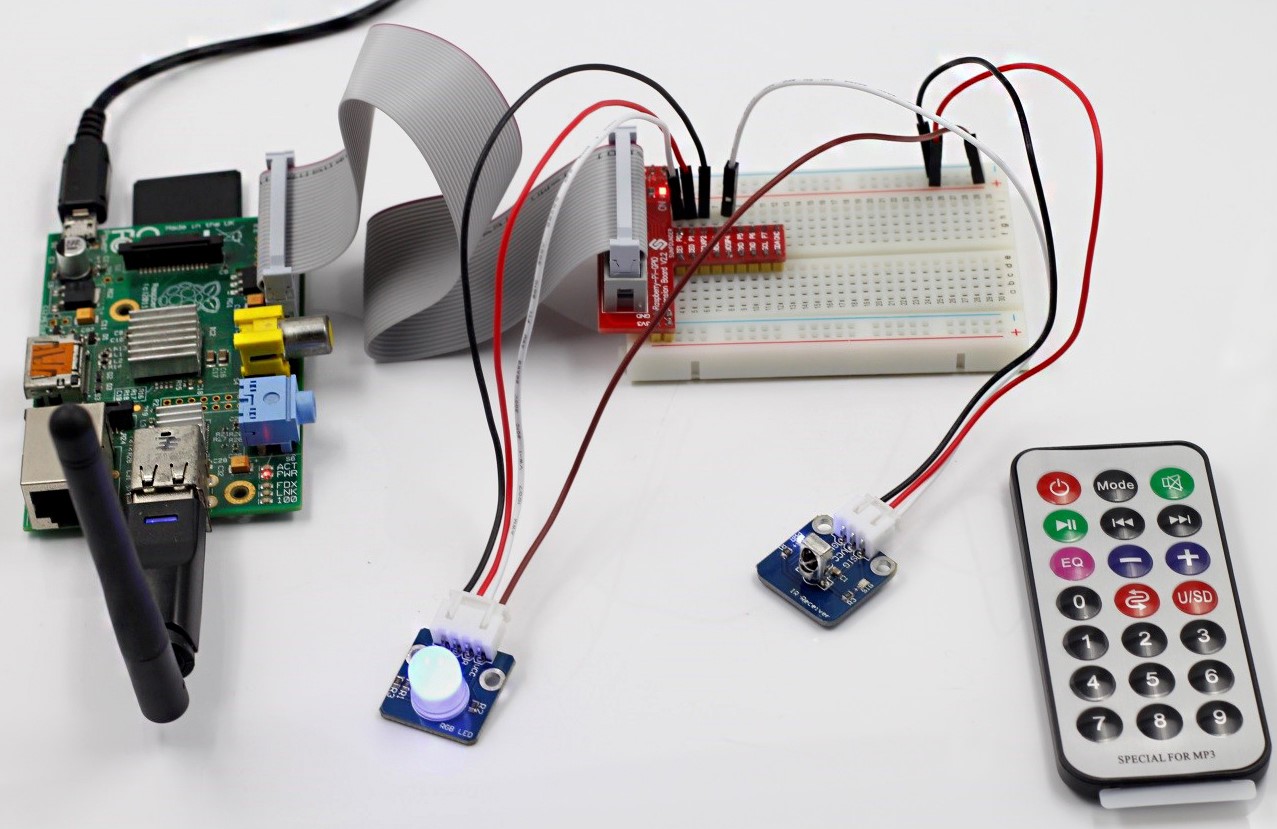
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | IR Receiver Module |
| GPIO4 | SIG |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| Raspberry Pi | RGB LED Module |
| 5V | VCC |
| GPIO0 | R |
| GPIO1 | G |
| GPIO2 | B |
Step 2: Download the LIRC library
sudo apt-get install lirc
Step 3: Set up lirc:
Open your /etc/modules file:
sudo nano /etc/modules
Add this to the end:
lirc_dev
lirc_rpi gpio_in_pin=23 gpio_out_pin=22
Press Ctrl +O and Ctrl +X, save and exit .
Edit the /etc/lirc/hardware.conffile:
sudo nano /etc/lirc/hardware.conf
Modify the file as shown below:
# Run “lircd –driver=help” for a list of supported drivers.
DRIVER=“default”
# usually /dev/lirc0 is the correct setting for systems using udev
DEVICE=“/dev/lirc0”
MODULES=“lirc_rpi”
Press Ctrl +O and Ctrl +X, save and exit.
Copy the remote configuration file lircd.conf to/home/pi and /etc/lirc:
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2
cp lircd.conf /home/pi
sudo cp lircd.conf /etc/lirc/
Open the /boot/config.txt file:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Add the following line to the end:
dtoverlay=lirc-rpi:gpio_in_pin=23,gpio_out_pin=22
Press Ctrl +O and Ctrl +X, save and exit .
Reboot the Raspberry Pi after the change.
sudo reboot
Step 4: Test the IR receiver
Check if lirc module is loaded:
ls /dev/li*
You should see this:
/dev/lirc0 /dev/lircd
Run the command to stop lircd and start outputting raw data from the IR receiver:
irw
When you press a button on the remote, you can see the button name printed on the screen.
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ irw
0000000000000001 00 KEY_CHANNELDOWN /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000002 00 KEY_CHANNEL /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000003 00 KEY_CHANNELUP /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000004 00 KEY_PREVIOUS /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000005 00 KEY_NEXT /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000006 00 KEY_PLAYPAUSE /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000007 00 KEY_VOLUMEDOWN /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000008 00 KEY_VOLUMEUP /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000009 00 KEY_EQUAL /home/pi/lircd.conf
000000000000000a 00 KEY_NUMERIC_0 /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000014 00 BTN_0 /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000015 00 BTN_1 /home/pi/lircd.conf
000000000000000b 00 KEY_NUMERIC_1 /home/pi/lircd.conf
000000000000000c 00 KEY_NUMERIC_2 /home/pi/lircd.conf
000000000000000d 00 KEY_NUMERIC_3 /home/pi/lircd.conf
000000000000000e 00 KEY_NUMERIC_4 /home/pi/lircd.conf
000000000000000f 00 KEY_NUMERIC_5 /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000010 00 KEY_NUMERIC_6 /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000011 00 KEY_NUMERIC_7 /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000012 00 KEY_NUMERIC_8 /home/pi/lircd.conf
0000000000000013 00 KEY_NUMERIC_9 /home/pi/lircd.conf
If it does not appear, somewhere may be incorrectly configured. Check again that you’ve connected everything and haven’t crossed any wires.
For C language users:
Step 5: Download LIRC client library:
sudo apt-get install liblircclient-dev
Step 6: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/23_ircontrol/
Step 7: Create a lirc directory under /etc/lirc/:
sudo mkdir /etc/lirc/lirc/
Copy the lircrc file to /etc/lirc/lirc/:
sudo cp lircrc /etc/lirc/lirc/
Step 8: Compile
gcc ircontrol.c –lwiringPi –llirc_client
Step 9: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 5: Download pylirc:
sudo apt-get install python-pylirc
Step 6: Change directory:
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 7: Run
sudo python 23_ircontrol.py
Each of the top three rows of buttons on the remote control represents a kind of color, i.e. red, green, and blue, top to bottom. Each column represents off, light, and dark. For example, press the second button (light) on the first row (red), and the LED will flash light red. You can use the remote to generate 27 colors in total (including all the LEDs off). Try to change the color of the RGB LED with the 9 buttons!
C Code
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <softPwm.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <lirc/lirc_client.h>
#include <time.h>
#define uchar unsigned char
#define LedPinRed 0
#define LedPinGreen 1
#define LedPinBlue 2
uchar color[3] = {0xff, 0xff, 0xff};
uchar Lv[3] = {0xff, 0x44, 0x00};
char *keymap[21] ={
" KEY_CHANNELDOWN ",
" KEY_CHANNEL ",
" KEY_CHANNELUP ",
" KEY_PREVIOUS ",
" KEY_NEXT ",
" KEY_PLAYPAUSE ",
" KEY_VOLUMEDOWN ",
" KEY_VOLUMEUP ",
" KEY_EQUAL ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_0 ",
" BTN_0 ",
" BTN_1 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_1 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_2 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_3 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_4 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_5 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_6 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_7 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_8 ",
" KEY_NUMERIC_9 "};
void ledInit(void)
{
softPwmCreate(LedPinRed, 0, 100);
softPwmCreate(LedPinGreen,0, 100);
softPwmCreate(LedPinBlue, 0, 100);
}
void ledColorSet()
{
softPwmWrite(LedPinRed, color[0]);
softPwmWrite(LedPinGreen, color[1]);
softPwmWrite(LedPinBlue, color[2]);
}
int key(char *code){
int i;
int num;
for (i=0; i<21; i++){
if (strstr(code, keymap[i])){
num = i;
}
}
return num + 1;
}
int RGB(int i){
switch(i){
case 1: color[0] = Lv[0]; printf("Red OFF\n"); break;
case 2: color[0] = Lv[1]; printf("Light Red\n"); break;
case 3: color[0] = Lv[2]; printf("Dark Red\n"); break;
case 4: color[1] = Lv[0]; printf("Green OFF\n"); break;
case 5: color[1] = Lv[1]; printf("Light Green\n"); break;
case 6: color[1] = Lv[2]; printf("Dark Green\n"); break;
case 7: color[2] = Lv[0]; printf("Blue OFF\n"); break;
case 8: color[2] = Lv[1]; printf("Light Blue\n"); break;
case 9: color[2] = Lv[2]; printf("Dark Green\n"); break;
}
}
int main(void)
{
struct lirc_config *config;
int buttonTimer = millis();
char *code;
char *c;
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
if(lirc_init("lirc",1)==-1)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
ledInit();
ledColorSet();
if(lirc_readconfig(NULL,&config,NULL)==0)
{
while(lirc_nextcode(&code)==0)
{
if(code==NULL) continue;{
if (millis() - buttonTimer > 400){
RGB(key(code));
ledColorSet(color);
}
}
free(code);
}
lirc_freeconfig(config);
}
lirc_deinit();
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/python
import pylirc, time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
Rpin = 17
Gpin = 18
Bpin = 27
blocking = 0;
Lv = [0, 20, 90] # Light Level
color = [0, 0, 0]
def setColor(color):
# global p_R, p_G, p_B
p_R.ChangeDutyCycle(100 - color[0]) # Change duty cycle
p_G.ChangeDutyCycle(100 - color[1])
p_B.ChangeDutyCycle(100 - color[2])
def setup():
global p_R, p_G, p_B
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(Rpin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(Gpin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(Bpin, GPIO.OUT)
p_R = GPIO.PWM(Rpin, 2000) # Set Frequece to 2KHz
p_G = GPIO.PWM(Gpin, 2000)
p_B = GPIO.PWM(Bpin, 2000)
p_R.start(100)
p_G.start(100)
p_B.start(100)
pylirc.init("pylirc", "./conf", blocking)
def map(x, in_min, in_max, out_min, out_max):
return (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min
def RGB(config):
global color
if config == 'KEY_CHANNELDOWN':
color[0] = Lv[0]
print 'Red OFF'
if config == 'KEY_CHANNEL':
color[0] = Lv[1]
print 'Light Red'
if config == 'KEY_CHANNELUP':
color[0] = Lv[2]
print 'Red'
if config == 'KEY_PREVIOUS':
color[1] = Lv[0]
print 'Green OFF'
if config == 'KEY_NEXT':
color[1] = Lv[1]
print 'Light Green'
if config == 'KEY_PLAYPAUSE':
color[1] = Lv[2]
print 'Green'
if config == 'KEY_VOLUMEDOWN':
color[2] = Lv[0]
print 'Blue OFF'
if config == 'KEY_VOLUMEUP':
color[2] = Lv[1]
print 'Light Blue'
if config == 'KEY_EQUAL':
color[2] = Lv[2]
print 'BLUE'
def loop():
while True:
s = pylirc.nextcode(1)
while(s):
for (code) in s:
# print 'Command: ', code["config"] #For debug: Uncomment this
# line to see the return value of buttons
RGB(code["config"])
setColor(color)
if(not blocking):
s = pylirc.nextcode(1)
else:
s = []
def destroy():
p_R.stop()
p_G.stop()
p_B.stop()
GPIO.output(Rpin, GPIO.HIGH) # Turn off all leds
GPIO.output(Gpin, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(Bpin, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.cleanup()
pylirc.exit()
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
setup()
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
