Introduction
A rotary encoder is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to analog or digital code. Rotary encoders are usually placed at the side which is perpendicular to the shaft. They act as sensors for detecting angle, speed, length, position, and acceleration in automation field.
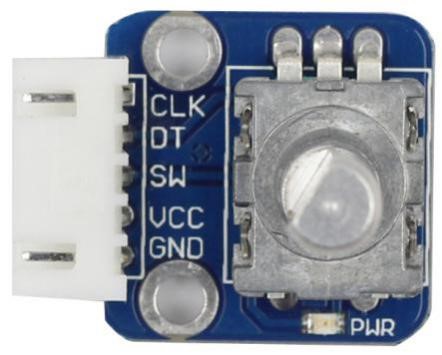
Components
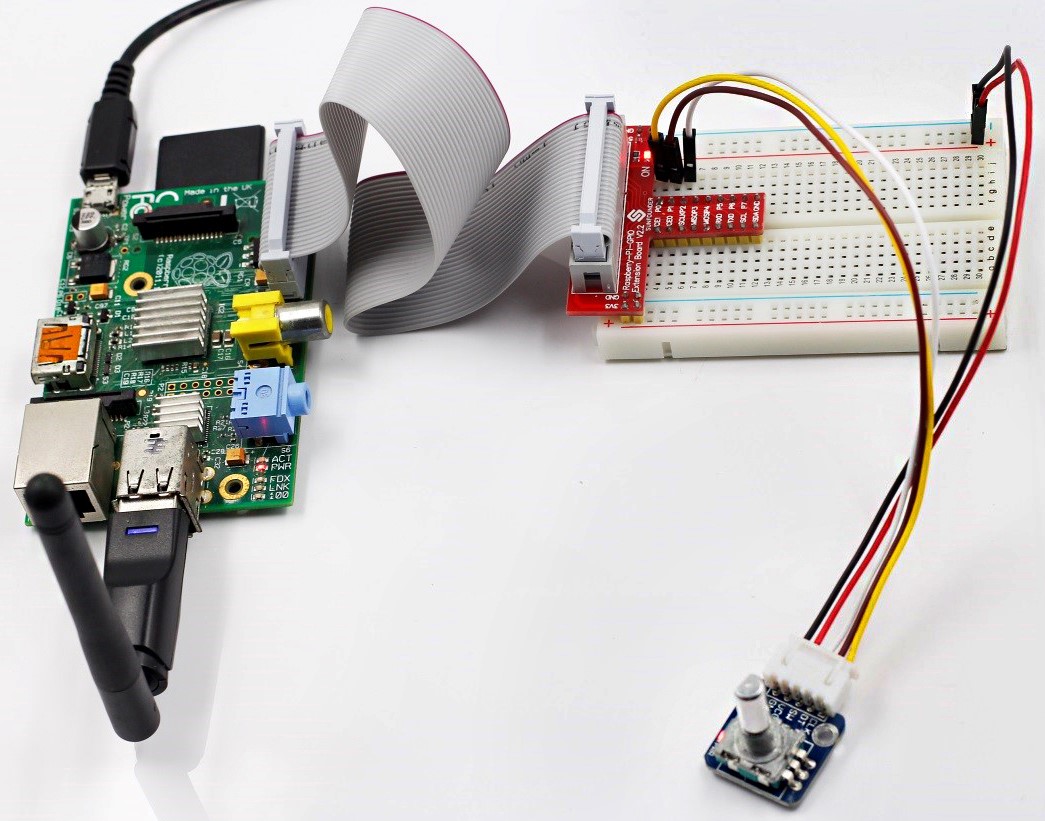
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * Rotary Encoder module
– 1 * 5-Pin Anti-reverse Cable
Experimental Principle
Most rotary encoders have 5 pins with three functions of turning left & right and pressing down. Pin 1 and pin 2 are switch wiring terminals used to press. They are similar to buttons previously mentioned, so we will no longer discuss them in this experiment. Pin 4 is generally connected to ground. Pin 3 and pin 5 are first connected to pull-up resistor and then to the microprocessor. In this experiment, they are connected to GPIO0 and GPIO1 of Raspberry Pi. When it is rotated left and right, there will be pulse inputs in pin 1 and pin 3.
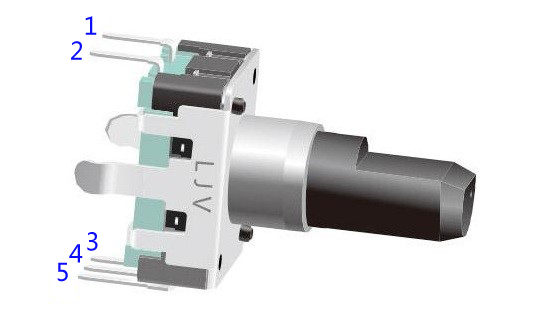
It shows that if output 1 is high and output 2 is high, then the switch rotates clockwise; if output 1 is high and output 2 is low, then the switch rotates counterclockwise. As a result, during SCM programming, if output 1 is high, then you can tell whether the rotary encoder rotates left or right as long as you know the state of output 2.
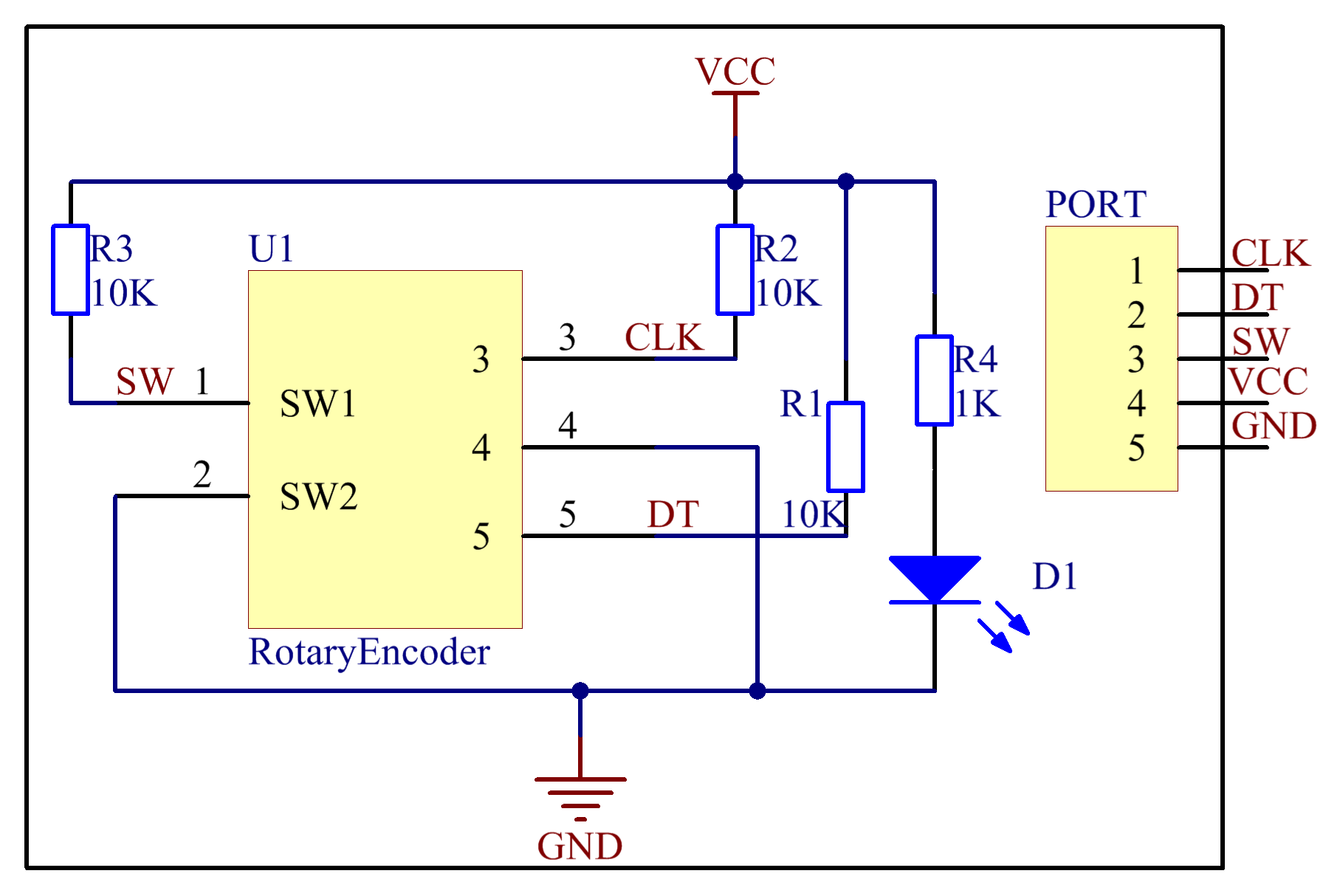
Experimental Procedures
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | Rotary Encoder module |
| GPIO0 | CLK |
| GPIO1 | DT |
| GPIO2 | SW |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
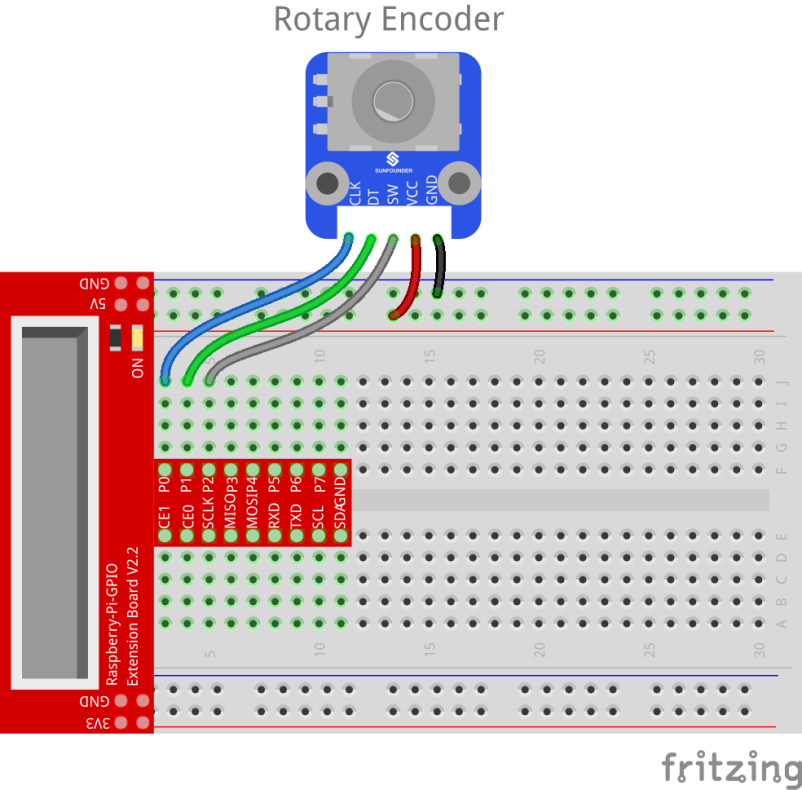
For C language users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/27_rotary_encoder/
Step 3: Compile
gcc rotary_encoder.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 3: Run
sudo python 27_rotary_encoder.py
Now rotate the shaft of the rotary encoder, and the value printed on the screen will change. Rotate the rotary encoder clockwise, the value will increase; Rotate it counterclockwise, the value will decrease; Press the rotary encoder, the value will be reset to 0.
C Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#define RoAPin 0
#define RoBPin 1
#define SWPin 2
static volatile int globalCounter = 0 ;
unsigned char flag;
unsigned char Last_RoB_Status;
unsigned char Current_RoB_Status;
void btnISR(void)
{
globalCounter = 0;
}
void rotaryDeal(void)
{
Last_RoB_Status = digitalRead(RoBPin);
while(!digitalRead(RoAPin)){
Current_RoB_Status = digitalRead(RoBPin);
flag = 1;
}
if(flag == 1){
flag = 0;
if((Last_RoB_Status == 0)&&(Current_RoB_Status == 1)){
globalCounter ++;
}
if((Last_RoB_Status == 1)&&(Current_RoB_Status == 0)){
globalCounter --;
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to setup wiringPi:%s\n",strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
pinMode(SWPin, INPUT);
pinMode(RoAPin, INPUT);
pinMode(RoBPin, INPUT);
pullUpDnControl(SWPin, PUD_UP);
if(wiringPiISR(SWPin, INT_EDGE_FALLING, &btnISR) < 0){
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to init ISR\n",strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
int tmp = 0;
while(1){
rotaryDeal();
if (tmp != globalCounter){
printf("%d\n", globalCounter);
tmp = globalCounter;
}
}
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
RoAPin = 11 # CLK Pin
RoBPin = 12 # DT Pin
BtnPin = 13 # Button Pin
globalCounter = 0
flag = 0
Last_RoB_Status = 0
Current_RoB_Status = 0
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(RoAPin, GPIO.IN) # input mode
GPIO.setup(RoBPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(BtnPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
def rotaryDeal():
global flag
global Last_RoB_Status
global Current_RoB_Status
global globalCounter
Last_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
while(not GPIO.input(RoAPin)):
Current_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
flag = 0
if (Last_RoB_Status == 0) and (Current_RoB_Status == 1):
globalCounter = globalCounter + 1
if (Last_RoB_Status == 1) and (Current_RoB_Status == 0):
globalCounter = globalCounter - 1
def btnISR(channel):
global globalCounter
globalCounter = 0
def loop():
global globalCounter
tmp = 0 # Rotary Temperary
GPIO.add_event_detect(BtnPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=btnISR)
while True:
rotaryDeal()
if tmp != globalCounter:
print 'globalCounter = %d' % globalCounter
tmp = globalCounter
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()