Introduction
An IR obstacle avoidance module (as shown below) uses infrared reflection principle to detect obstacles. When there is no object ahead, infrared-receiver cannot receive signals; when there is an object ahead, it will block and reflect infrared light, then infrared-receiver can receive signals.
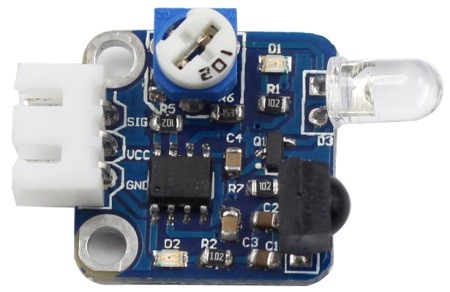
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * IR Obstacle module
– 1 * 3-Pin anti-reverse cable
Experimental Principle
An obstacle avoidance sensor mainly consists of an infrared-transmitter, an infrared-receiver and a potentiometer. According to the reflecting feature of an object, if there is no obstacle, emitted infrared ray will weaken with the propagation distance and finally disappear. If there is an obstacle, when infrared ray encounters an obstacle, it will be reflected back to the infrared-receiver. Then the infrared-receiver detects this signal and confirms an obstacle exists ahead.
Note: The detection distance of the infrared sensor is adjustable – you may adjust it by the potentiometer.
The schematic diagram:
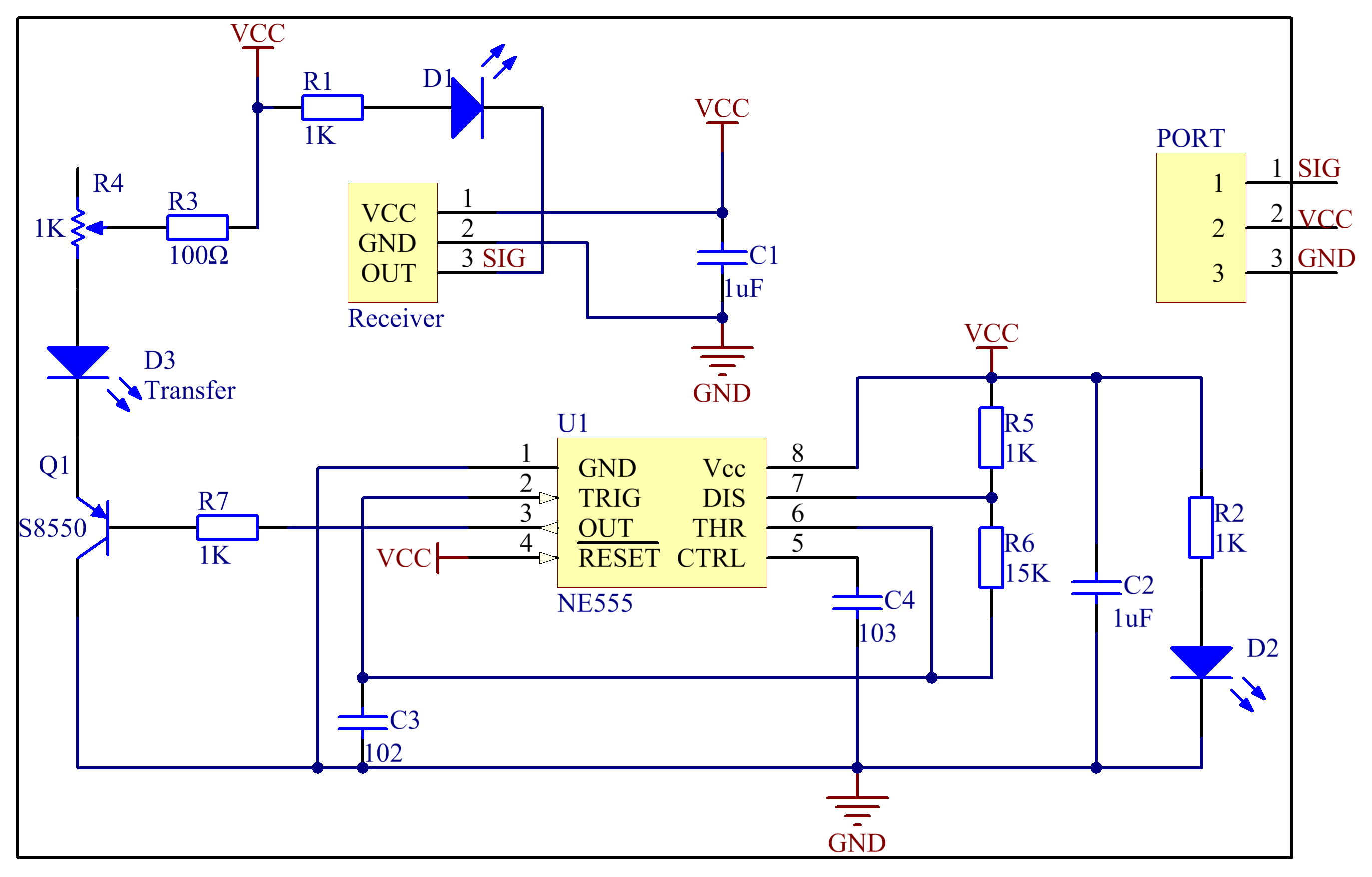
Experimental Procedures
Step 1: Build the circuit
| Raspberry Pi | IR Obstacle Module |
| GPIO0 | SIG |
| 5V | VCC |
| GND | GND |
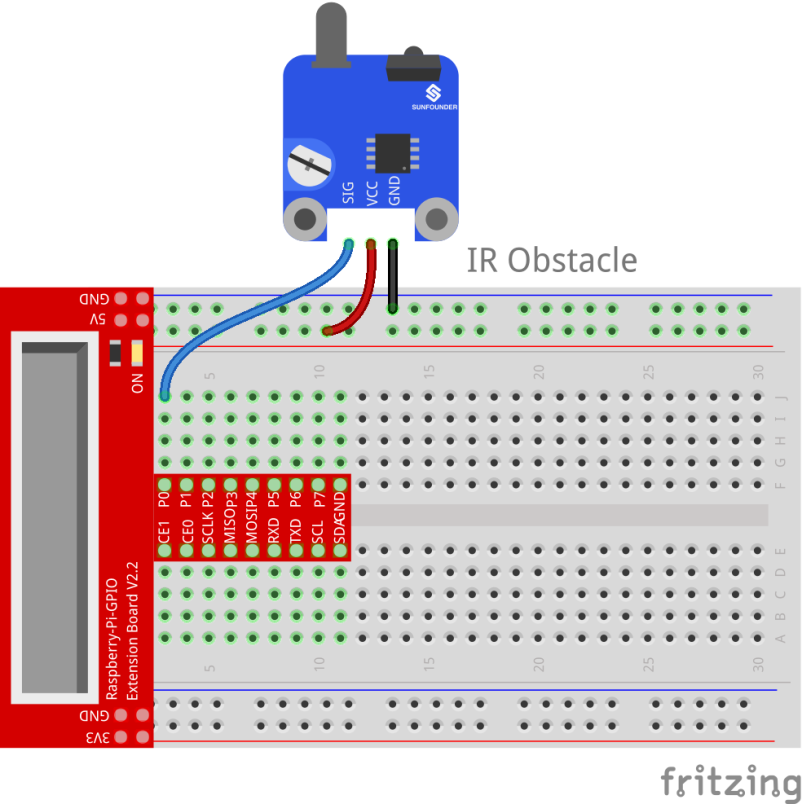
For C language users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/29_ir_obstacle/
Step 3: Compile
gcc ir_obstacle.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
sudo ./a.out
For Python users:
Step 2: Change directory
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 3: Run
sudo python 29_ir_obstacle.py
Now, if there is an obstacle ahead, a string “Detected Barrier!” will be printed on the screen.
C Code
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ObstaclePin 0
void myISR(void)
{
printf("Detected Barrier !\n");
}
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print messageto screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !\n");
return 1;
}
if(wiringPiISR(ObstaclePin, INT_EDGE_FALLING, &myISR) < 0){
printf("Unable to setup ISR !!!\n");
return 1;
}
while(1){
;
}
return 0;
}
Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python import RPi.GPIO as GPIO ObstaclePin = 11 def setup(): GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location GPIO.setup(ObstaclePin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) def loop(): while True: if (0 == GPIO.input(ObstaclePin)): print "Detected Barrier!" def destroy(): GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here setup() try: loop() except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed. destroy()
