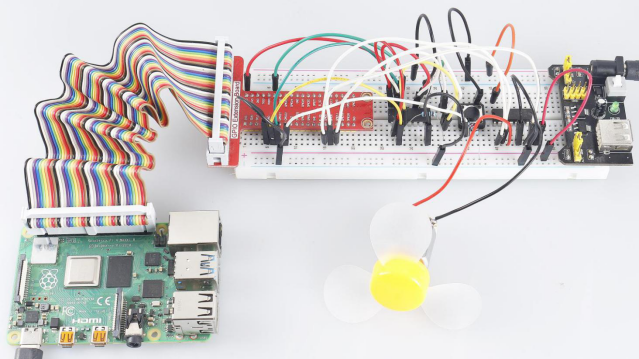
Introduction
In this course, we will use motors, buttons and thermistors to make a manual + automatic smart fan whose wind speed is adjustable.
Components
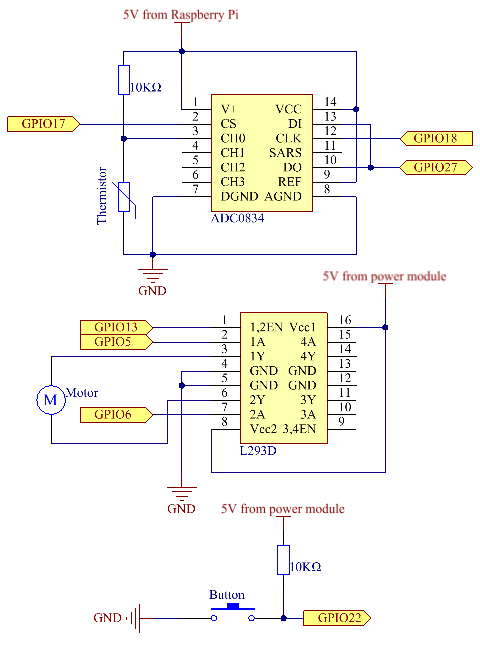
Schematic Diagram
| T-Board Name | physical | wiringPi | BCM |
| GPIO17 | Pin 11 | 0 | 17 |
| GPIO18 | Pin 12 | 1 | 18 |
| GPIO27 | Pin 13 | 2 | 27 |
| GPIO22 | Pin 15 | 3 | 22 |
| GPIO5 | Pin 29 | 21 | 5 |
| GPIO6 | Pin 31 | 22 | 6 |
| GPIO13 | Pin 33 | 23 | 13 |
Experimental Procedures
Step 1: Build the circuit.
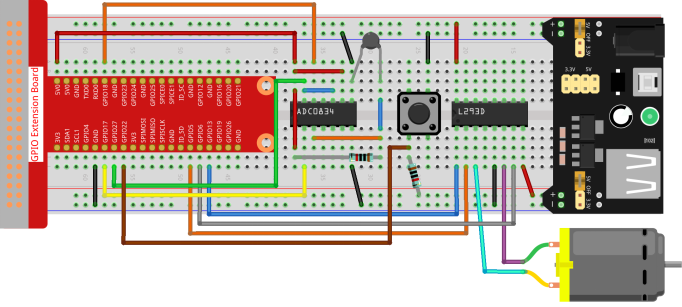
Note: The power module can apply a 9V battery with the 9V Battery Buckle in the kit. Insert the jumper cap of the power module into the 5V bus strips of the breadboard.

- For C Language Users
Step 2: Get into the folder of the code.
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/c/3.1.4/Step 3: Compile.
gcc 3.1.4_SmartFan.c -lwiringPi -lmStep 4: Run the executable file above.
sudo ./a.outAs the code runs, start the fan by pressing the button. Every time you press, 1 speed grade is adjusted up or down. There are 5 kinds of speed grades: 0~4. When set to the 4th speed grade and you press the button, the fan stops working with a 0 wind speed.
Once the temperature goes up or down for more than 2℃, the speed automatically gets 1-grade faster or slower.
Code Explanation
int temperture(){
unsigned char analogVal;
double Vr, Rt, temp, cel, Fah;
analogVal = get_ADC_Result(0);
Vr = 5 * (double)(analogVal) / 255;
Rt = 10000 * (double)(Vr) / (5 - (double)(Vr));
temp = 1 / (((log(Rt/10000)) / 3950)+(1 / (273.15 + 25)));
cel = temp - 273.15;
Fah = cel * 1.8 +32;
int t=cel;
return t;
}Temperture() works by converting thermistor values read by ADC0834 into temperature values. Refer to 2.2.2 Thermistor for more details.
int motor(int level){
if(level==0){
digitalWrite(MotorEnable,LOW);
return 0;
}
if (level>=4){
level =4;
}
digitalWrite(MotorEnable,HIGH);
softPwmWrite(MotorPin1, level*25);
return level;
}This function controls the rotating speed of the motor. The range of the Level: 0-4 (level 0 stops the working motor). One level adjustment stands for a 25% change of the wind speed.
int main(void)
{
setup();
int currentState,lastState=0;
int level = 0;
int currentTemp,markTemp=0;
while(1){
currentState=digitalRead(BtnPin);
currentTemp=temperture();
if (currentTemp<=0){continue;}
if (currentState==1&&lastState==0){
level=(level+1)%5;
markTemp=currentTemp;
delay(500);
}
lastState=currentState;
if (level!=0){
if (currentTemp-markTemp<=-2){
level=level-1;
markTemp=currentTemp;
}
if (currentTemp-markTemp>=2){
level=level+1;
markTemp=currentTemp;
}
}
level=motor(level);
}
return 0;
}The function main() contains the whole program process as shown:
- Constantly read the button state and the current temperature.
- Every press makes level+1 and at the same time, the temperature is updated. The Level ranges 1~4.
- As the fan works ( the level is not 0), the temperature is under detection. A 2℃+ change causes the up and down of the level.
- The motor changes the rotating speed with the Level.
- For Python Language Users
Step 2: Get into the folder of the code.
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/pythonStep 3: Run.
sudo python3 3.1.4_SmartFan.pyAs the code runs, start the fan by pressing the button. Every time you press, 1 speed grade is adjusted up or down. There are 5 kinds of speed grades: 0~4. When set to the 4th speed grade and you press the button, the fan stops working with a 0 wind speed.
Once the temperature goes up or down for more than 2℃, the speed automatically gets 1-grade faster or slower.
Code Explanation
def temperature():
analogVal = ADC0834.getResult()
Vr = 5 * float(analogVal) / 255
Rt = 10000 * Vr / (5 - Vr)
temp = 1/(((math.log(Rt / 10000)) / 3950) + (1 / (273.15+25)))
Cel = temp - 273.15
Fah = Cel * 1.8 + 32
return Celtemperture() works by converting thermistor values read by ADC0834 into temperature values. Refer to 2.2.2 Thermistor for more details.
def motor(level):
if level == 0:
GPIO.output(MotorEnable, GPIO.LOW)
return 0
if level>=4:
level = 4
GPIO.output(MotorEnable, GPIO.HIGH)
p_M1.ChangeDutyCycle(level*25)
return levelThis function controls the rotating speed of the motor. The range of the Lever: 0-4 (level 0 stops the working motor). One level adjustment stands for a 25% change of the wind speed.
def main():
lastState=0
level=0
markTemp = temperature()
while True:
currentState =GPIO.input(BtnPin)
currentTemp=temperature()
if currentState == 1 and lastState == 0:
level=(level+1)%5
markTemp = currentTemp
time.sleep(0.5)
lastState=currentState
if level!=0:
if currentTemp-markTemp <= -2:
level = level -1
markTemp=currentTemp
if currentTemp-markTemp >= 2:
level = level +1
markTemp=currentTemp
level = motor(level)The function main() contains the whole program process as shown:
- Constantly read the button state and the current temperature.
- Every press makes level+1 and at the same time, the temperature is updated. The Level ranges 1~4.
- As the fan works ( the level is not 0), the temperature is under detection. A 2℃+ change causes the up and down of the level.
- The motor changes the rotating speed with the Level.
Phenomenon Picture