Introduction
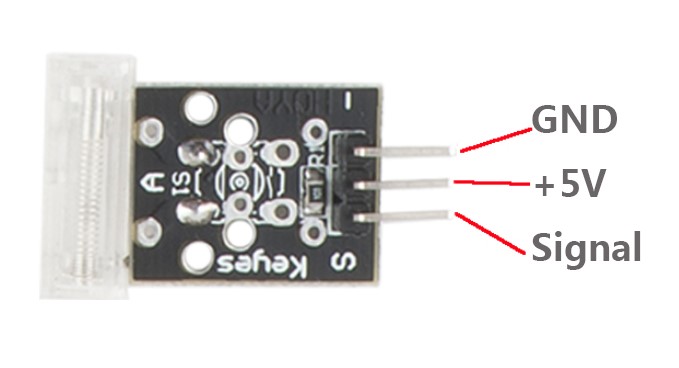
A knock sensor (as shown below) is similar to a shock switch. Being more sensitive, it can feel slighter vibrations.
Components
– 1 * Raspberry Pi
– 1 * Breadboard
– 1 * Network cable (or USB wireless network adapter)
– 1 * Knock sensor module
– 1 * Dual-color Common-Cathode LED module
– Several jumper wires
Experimental Principle
It’s similar to the shock switch. When you knock the sensor, the two spring leaves will get touched and the circuit will conduct. At the same time, pin S will output Low. In this experiment, we will judge the knock signal by detecting the output voltage. A dual-color LED module is used to indicate knock signals. When the knock switch generates knock signals, the LED will light up.
Experimental Procedures
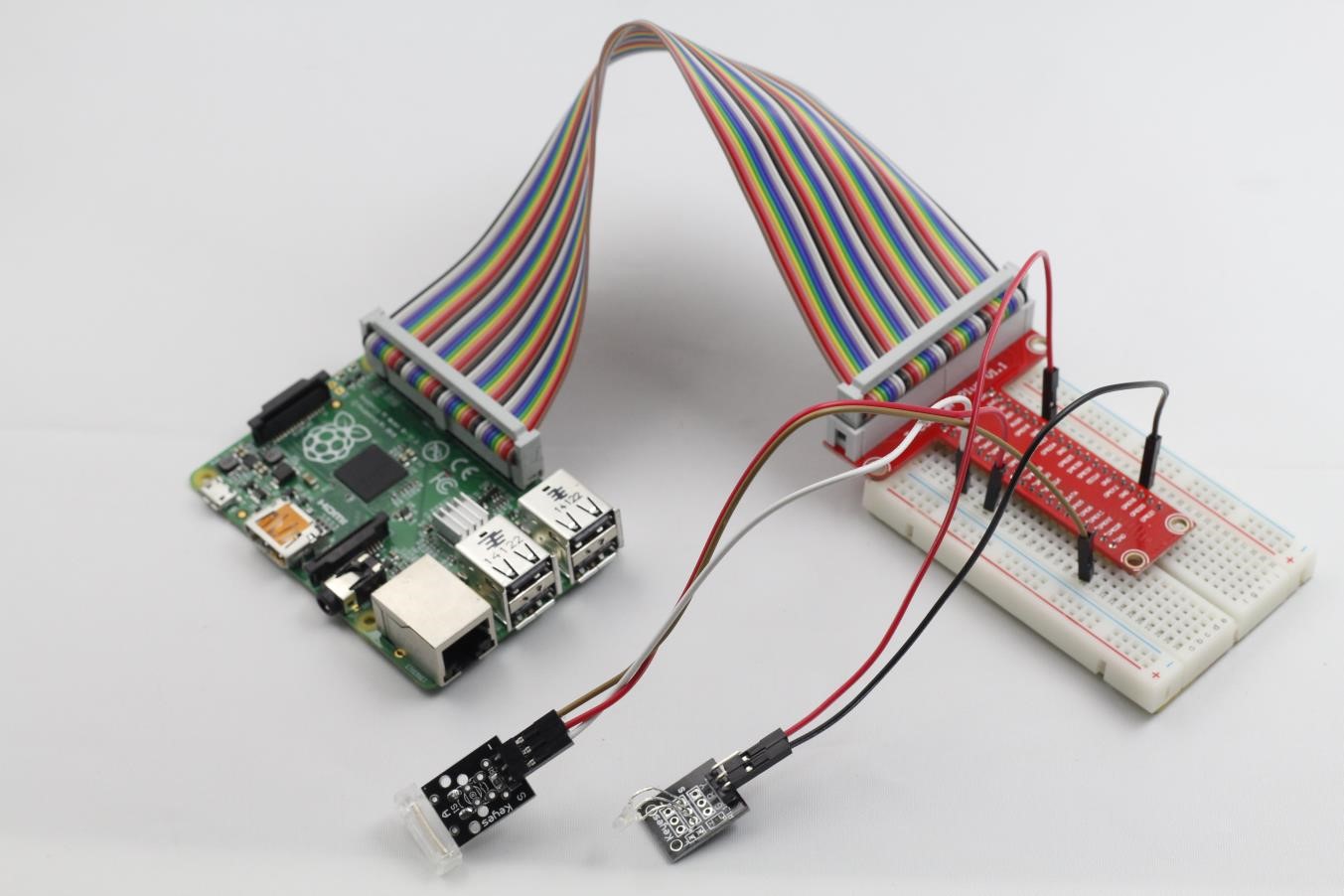
Step 1: Build the circuit
Knock switch connection: connect pin S of the knock switch module to GPIO0 of the Raspberry Pi; GND to GND; pin + to 3.3V
Dual-color LED module connection: connect pin R of the dual-color LED module to GPIO1 of the Raspberry Pi; GND to GND
Step 2: Edit and save the code (see path/Rpi_SensorKit_code/07_knockSensor/knockSensor.c)
Step 3: Compile
gcc knockSensor.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run
./a.out
Shake the sensor. Then pin S will output low level and you will see “Detected knocking” displayed on the screen, and the LED will light up.

knockSensor.c
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define KnockPin 0
#define LedPin 1
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print messageto screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
pinMode(KnockPin, INPUT);
pinMode(LedPin, OUTPUT);
while(1){
if(digitalRead(KnockPin) == LOW){
printf("Detected knocking!\n");
//digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW); //led on
digitalWrite(LedPin, !digitalRead(LedPin)); //led on
}
}
return 0;
}Python Code
#!/usr/bin/env python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
KnockPin = 11
LedPin = 12
Led_status = 1
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set LedPin's mode is output
GPIO.setup(KnockPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.HIGH) # Set LedPin high(+3.3V) to off led
def swLed(ev=None):
global Led_status
Led_status = not Led_status
GPIO.output(LedPin, Led_status) # switch led status(on-->off; off-->on)
print "LED: " + ("on" if Led_status else "off")
def loop():
GPIO.add_event_detect(KnockPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=swLed, bouncetime=200) # wait for falling
while True:
pass # Don't do anything
def destroy():
GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.LOW) # led off
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()